- Capabilities
- Getting started
- Architecture center
- Platform updates
Announcements
REMINDER: Sign up for the Foundry Newsletter to receive a summary of new products, features, and improvements across the platform directly to your inbox. For more information on how to subscribe, see the Foundry Newsletter and Product Feedback channels announcement.
Share your thoughts about these announcements in our Developer Community Forum ↗.
Configure Palantir for consumer mode and build external-facing applications
Date published: 2025-08-28
Optimize your Palantir environment for external users by configuring consumer mode in Foundry. Consumer mode is a powerful capability that enables organizations to deliver secure, scalable applications to external users. With consumer mode, you can build consumer-facing applications, including B2C and B2B solutions, while containing users within specific applications without broader platform access. Consumer mode configurations eliminate the need to grant extensive platform permissions to consumer users, allowing you to build external-facing applications backed by the Ontology without needing to manage infrastructure outside Foundry.
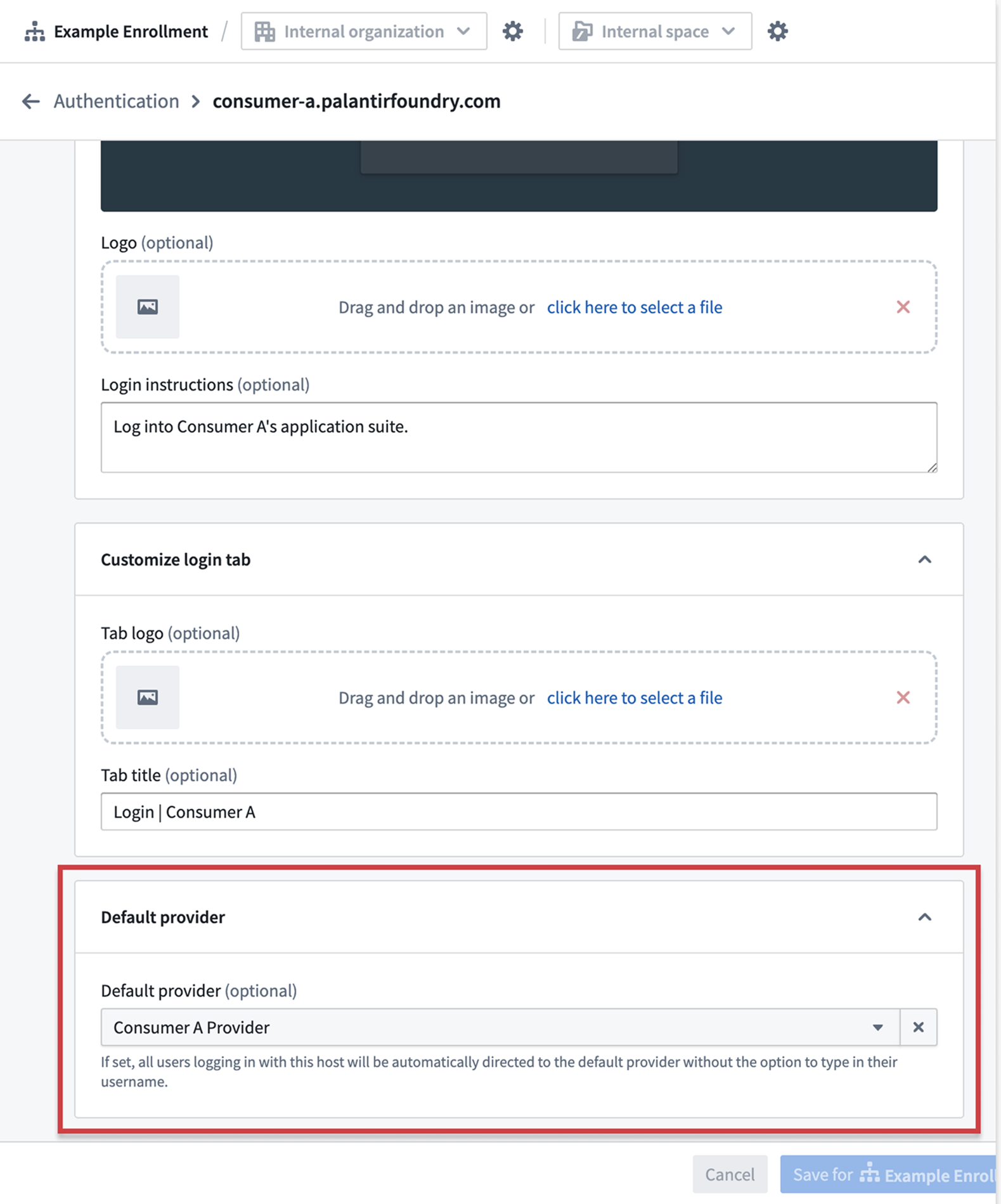
Set a default provider for user login when accessing the platform in consumer mode.
To get started, follow the documentation on how to configure Foundry for consumer mode. You will create dedicated consumer organizations and spaces, set up consumer authentication providers with automatic organization triaging, and configure restricted platform access.
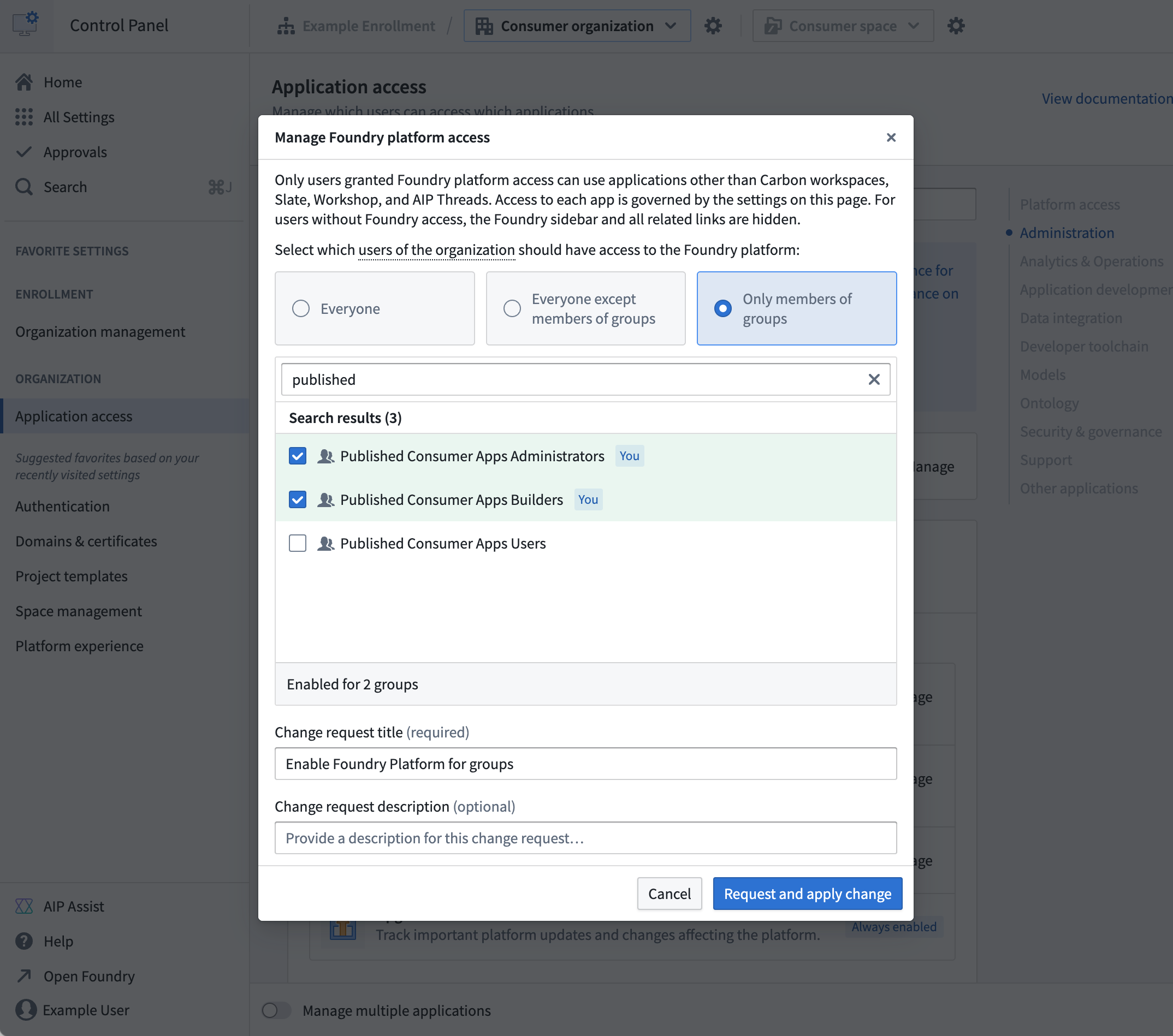
Manage platform access for consumer users in Control Panel.
Once Foundry is configured to use consumer mode, review three example deployment patterns for consumer applications to build and share with external users:
- In-platform applications using Workshop, Slate, or Carbon for rapid development.
- OAuth applications hosted on Foundry subdomains for pro-code solutions.
- Client credentials applications for externally-hosted services requiring maximum scale. The system enforces security through application access restrictions, minimal API permissions, and user isolation within private organizations.
Share your feedback
We want to hear about your experience using consumer mode to host external-facing applications. Let us know in our Foundry Support channels, or leave a post in our Developer Community ↗ using the control-panel ↗ tag.
GPT-5, GPT-5 mini, GPT-5 nano (Azure, Direct OpenAI) and Opus 4.1 (Google Vertex, Amazon Bedrock) are now available in AIP
Date published: 2025-08-21
GPT-5, GPT-5 mini, GPT-5 nano from OpenAI are now available for general use in AIP for enrollments with Azure and/or Direct OpenAI enabled in the US, EU, or non geo-restricted regions. GPT-5 is best suited for complex, real-world tasks across coding, writing, health, and multimodal reasoning, delivering expert-level intelligence, reduced hallucinations, and advanced instruction following. GPT-5 mini is the faster, more cost-efficient version of GPT-5 which is great for well-defined tasks and precise prompts. GPT-5 nano is ideal for summarization and classification tasks. Comparisons between the GPT-5 series models can be found in OpenAI's documentation↗.
Claude Opus 4.1 is Anthropic’s leading hybrid reasoning model, designed for demanding coding, agentic search, and AI agent tasks. With a 200K context window and advanced step-by-step reasoning, Opus 4.1 excels at complex, multi-step engineering and business challenges, offering superior code generation, long-horizon task management, and highly accurate, human-like writing. Enrollments with either Amazon Bedrock or Google Vertex enabled can start to use the Opus 4.1 model through AIP. Comparisons between Opus 4.1 and other models in the Anthropic family can be found in the Anthropic documentation↗.
As with all new models, use-case-specific evaluations are the best way to benchmark performance on your task.
For a list of all the models available in AIP, review the documentation.
Other recently added models to AIP
Google Vertex
- Gemini 2.5
- Gemini 2.5 Flash
- Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
xAI
- Grok-4
Your feedback matters
We want to hear about your experiences using language models in the Palantir platform and welcome your feedback. Share your thoughts with Palantir Support channels or on our Developer Community ↗ using the language-model-service tag ↗.
Extend Workshop module development with custom widgets
Date published: 2025-08-21
Custom widgets allow technical users to write custom frontend code to be securely rendered into Workshop. By building with code when necessary, these users can raise the development ceiling of typical low-code Workshop applications. Custom widgets will be generally available across enrollments in the coming weeks.
Users can build custom widgets to display complex visualizations and workflows, including the following examples:
- Custom chart visualizations, such a candlestick charts.
- Industry-specific views of an ontology object, like a flight plan
- Signature entry widgets
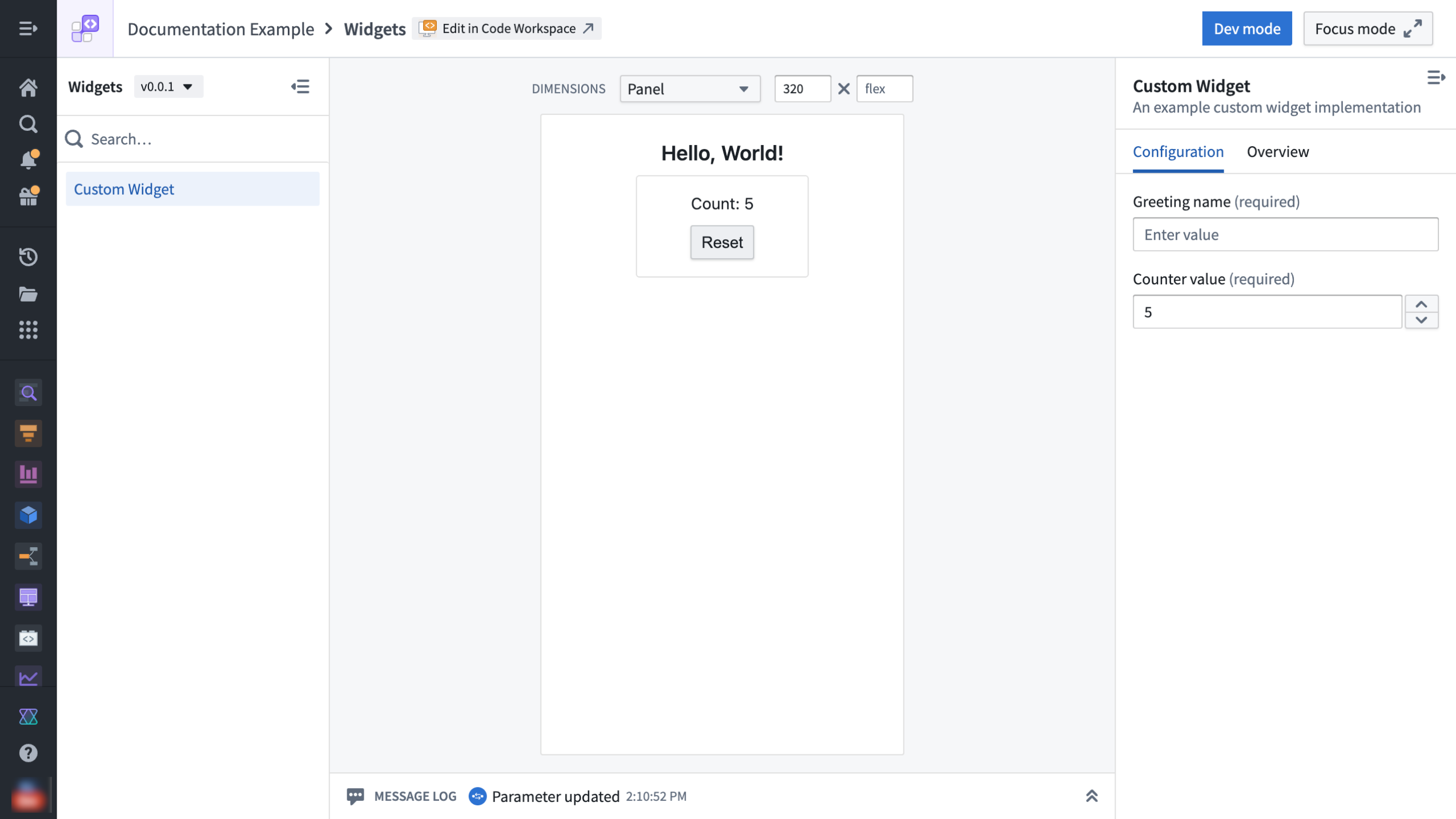
A custom widget in developer mode, offering a dedicated development environment for testing widgets.
Benefits of custom widgets
- Security: When you build custom frontend code, it is securely rendered and isolated from the main Foundry page.
- First-class developer tooling: Custom widgets offer advanced tooling for developers, including CLIs, a dedicated developer mode, and new libraries, so building widgets feels easy and natural.
- Indexing: Custom widgets are indexed so users can discover them through search for reuse across multiple applications.
When should I use custom widgets?
Currently, you can embed a website built in Developer Console through a Workshop iframe widget. Custom widgets improve this workflow by reducing the complexity of requiring OAuth and subdomain registration, while adding advanced developer tooling. However, you should continue to use iframe widgets to host Developer Console websites for standalone custom applications where a dedicated application subdomain, full control of the page, and advanced features like a customizable Content Security Policy (CSP) are required.
What's next?
We are currently working on several improvements to custom widgets that we plan to release soon:
- Marketplace integration
- Ability to use object set parameter types
- Developer mode improvements
- Widget startup performance
What do you think?
We welcome your feedback on your experience using custom widgets in your enrollment. Contact our Palantir Support channels, or create a post in our Developer Community ↗ using the custom-widgets↗ tag.
Easily drag and drop to reorder objects in the Object List widget
Date published: 2025-08-21
Workshop builders can now drag and drop object cards to reorder items within a single Object List widget. This new feature allows you to manually apply your own ordering of objects.
The reordering of objects in the widget is backed by an array of the primary keys of the sorted objects. The ordering of these primary keys in the array determines the display order of these objects in the sorted section of the widget. Any objects with primary keys not in the array are displayed in the Unsorted List section of the widget, located below the sorted objects.
Builders can choose to update the primary key array variable on reorder, or configure an action to trigger on each reorder.
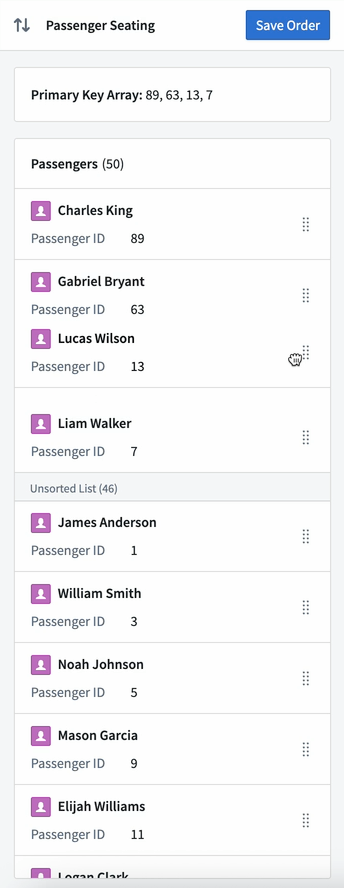
An Object List widget with reordering enabled, a Markdown widget displaying the primary key array backing the sort order, and a Button Group widget with a configured Action to save the updated primary key array’s values.
To learn more about how reordering configuration, its current limitations, and additional information, review our documentation.
New array variable transform operations are available in Workshop
Date published: 2025-08-21
We are excited to introduce new array variable transform operations for building in Workshop. These new operations offer Workshop builders even more ways to pull information from data to use in Workshop modules.
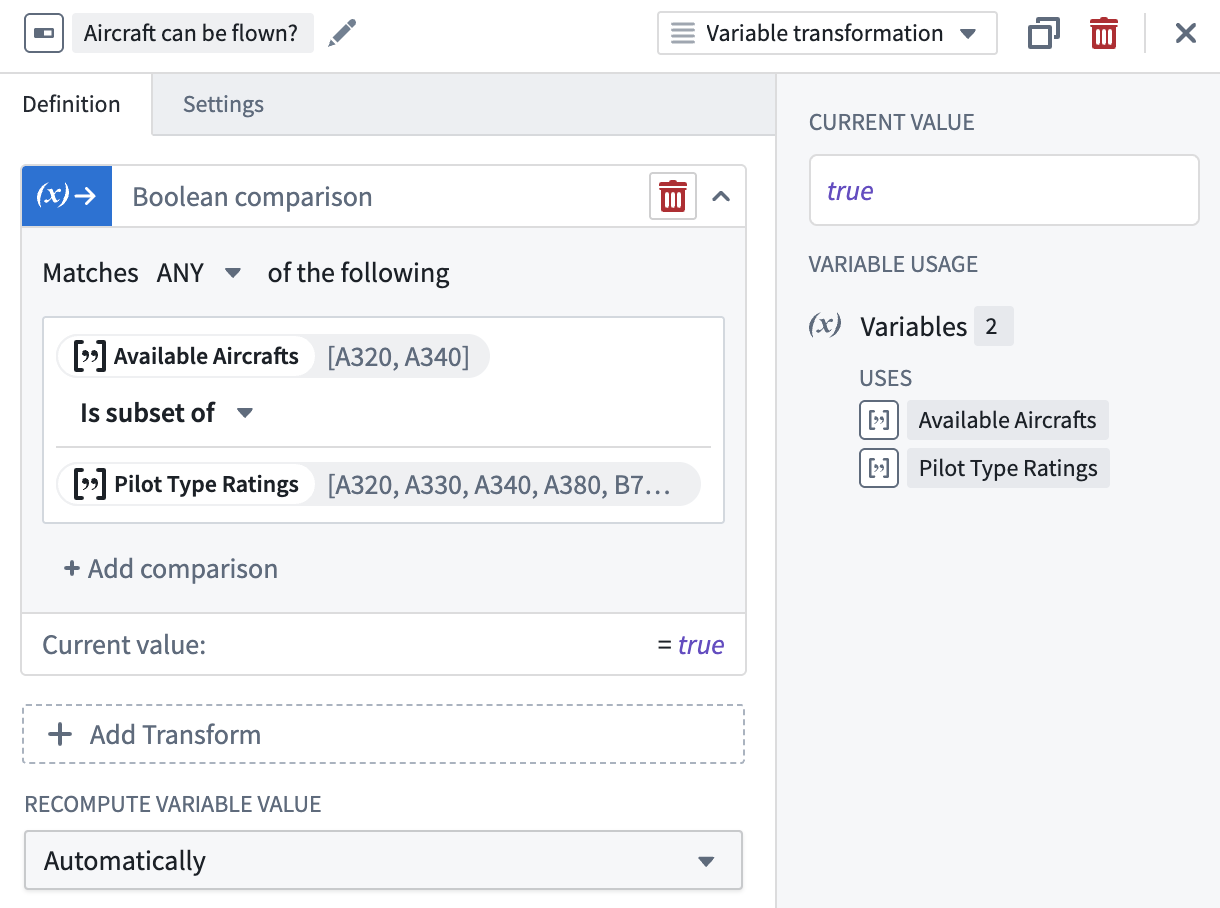
Is subset of
Use the Is subset of operation to check if a given array is a subset of another given array. A Boolean value will be returned.
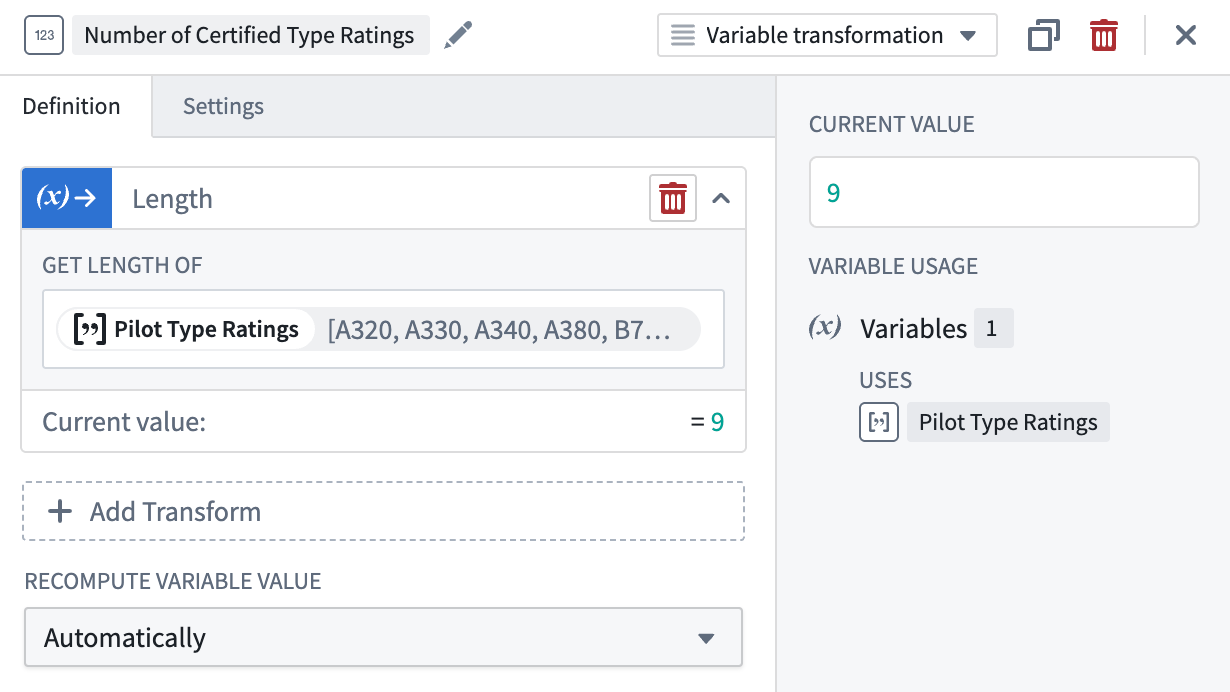
Length
The Length operation easily returns the length of an array. The returned numeric value represents the number of elements within the array.
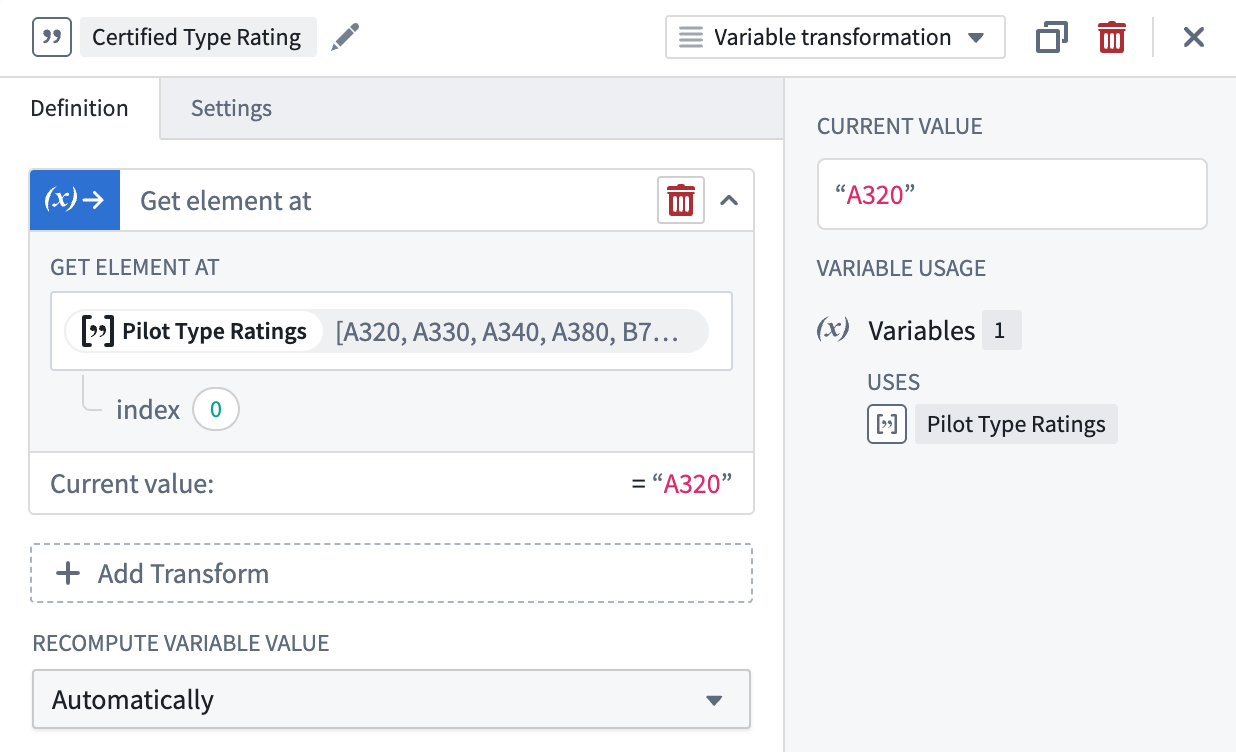
Get element at
Use the Get element at operation to grab an element within an array by specifying an index representing the element’s position in the array. A value matching the inputted array’s type will be returned.
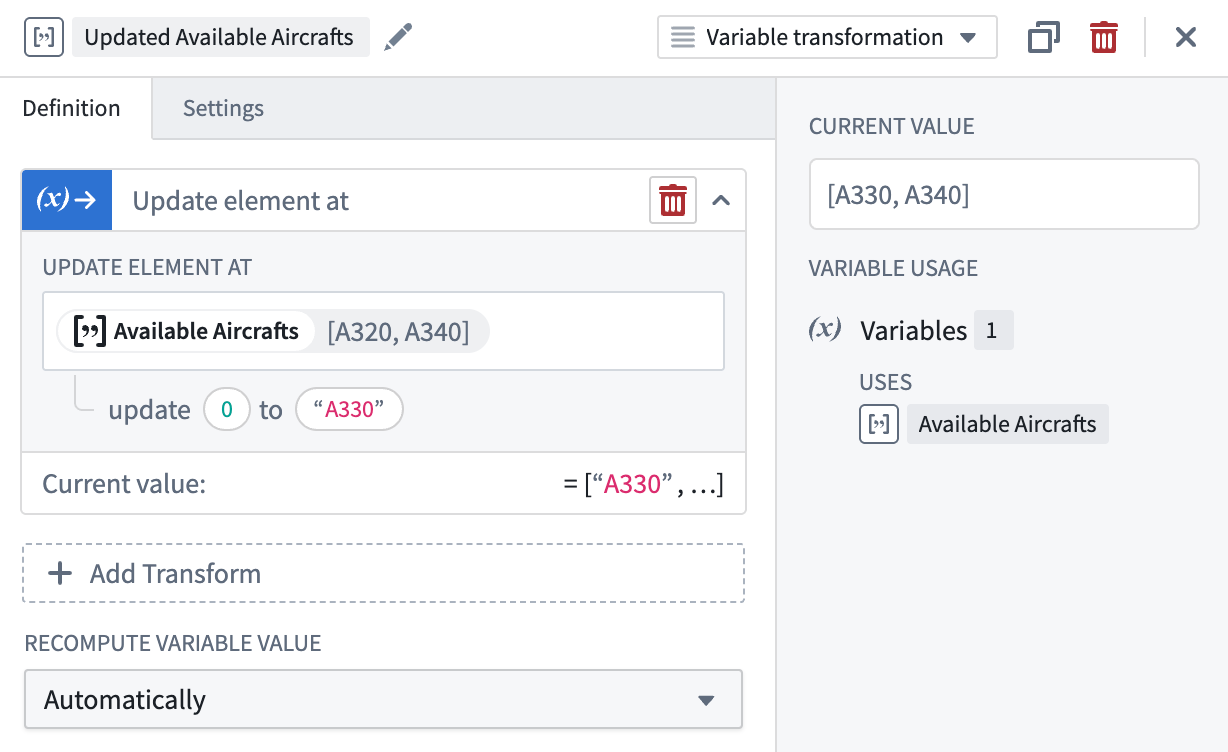
Update element at
The Update element at operation updates a specific element within the array by specifying an index representing the element’s position and a new entry matching the array’s type. The returned updated array matches the inputted array’s type.
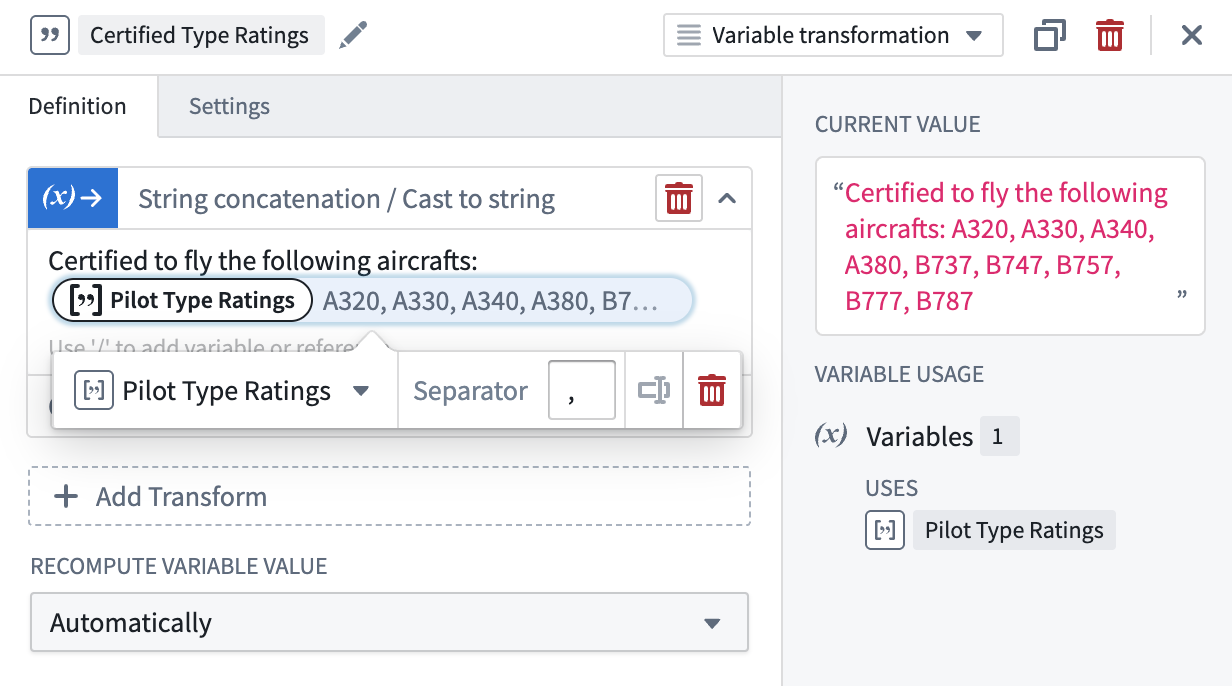
String concatenation/Cast to string
The String concatenation/cast to string operation can concatenate and cast elements within an array into a string, with an optional separator input added between elements.
Share your feedback
Let us know what you think about our new array variable transform operations by contacting our Palantir Support channels or posting your feedback in our Developer Community ↗ using the workshop ↗ tag
Expanded checkpoint strategy support in Pipeline Builder
Date published: 2025-08-21
Pipeline Builder now supports three checkpoints strategies, giving you flexible ways to save intermediate results within your pipeline. A checkpoint allows shared logic to be computed just once, even when multiple outputs rely on it. Therefore, using checkpoints can significantly reduce build times and improve efficiency for complex pipelines.
Checkpoint strategies:
-
Save in short-term disk (Default): Stores every output on disk temporarily. This is the default strategy for nodes marked as checkpoints.
-
Save in memory (Fastest): Stores results temporarily in memory for faster access; this is especially useful for small datasets. Note that this option may fail for larger datasets due to memory limitations.
-
Save as output data: Saves the latest transaction of the checkpoint in a dedicated dataset. The dataset is created upon the first deployment of the checkpoint.
You can now choose the checkpointing method that best fits your workflow and data requirements.
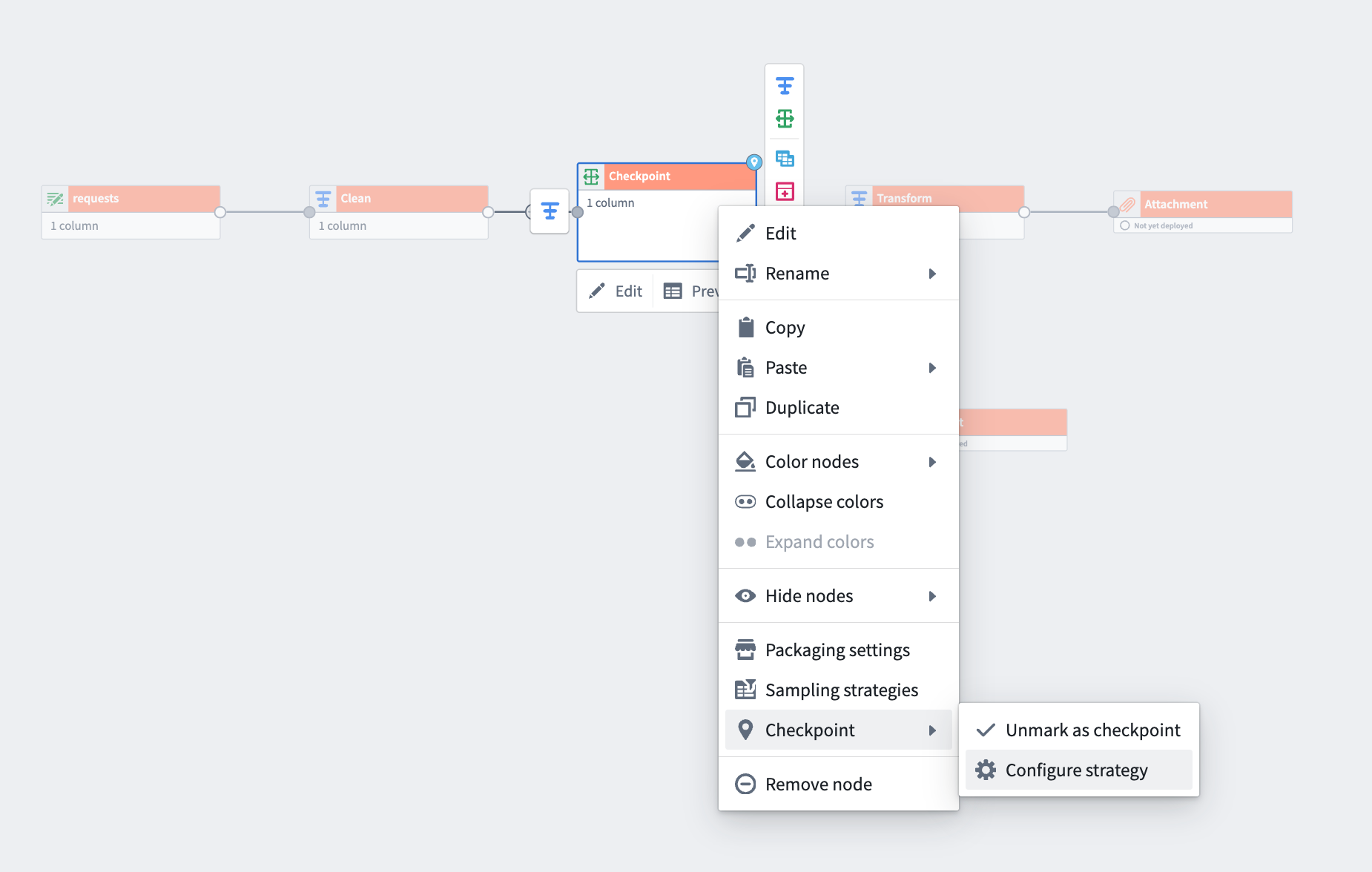
Right-click a transform node, select Checkpoint > Mark as checkpoint and then Configure strategy*.*
How to select a checkpoint strategy:
-
Right-click any transform node and select Mark as checkpoint.
-
From the same menu, use Configure strategy to choose your preferred checkpoint storage method for each output.
For nodes with multiple outputs, you can select a different strategy for each one.
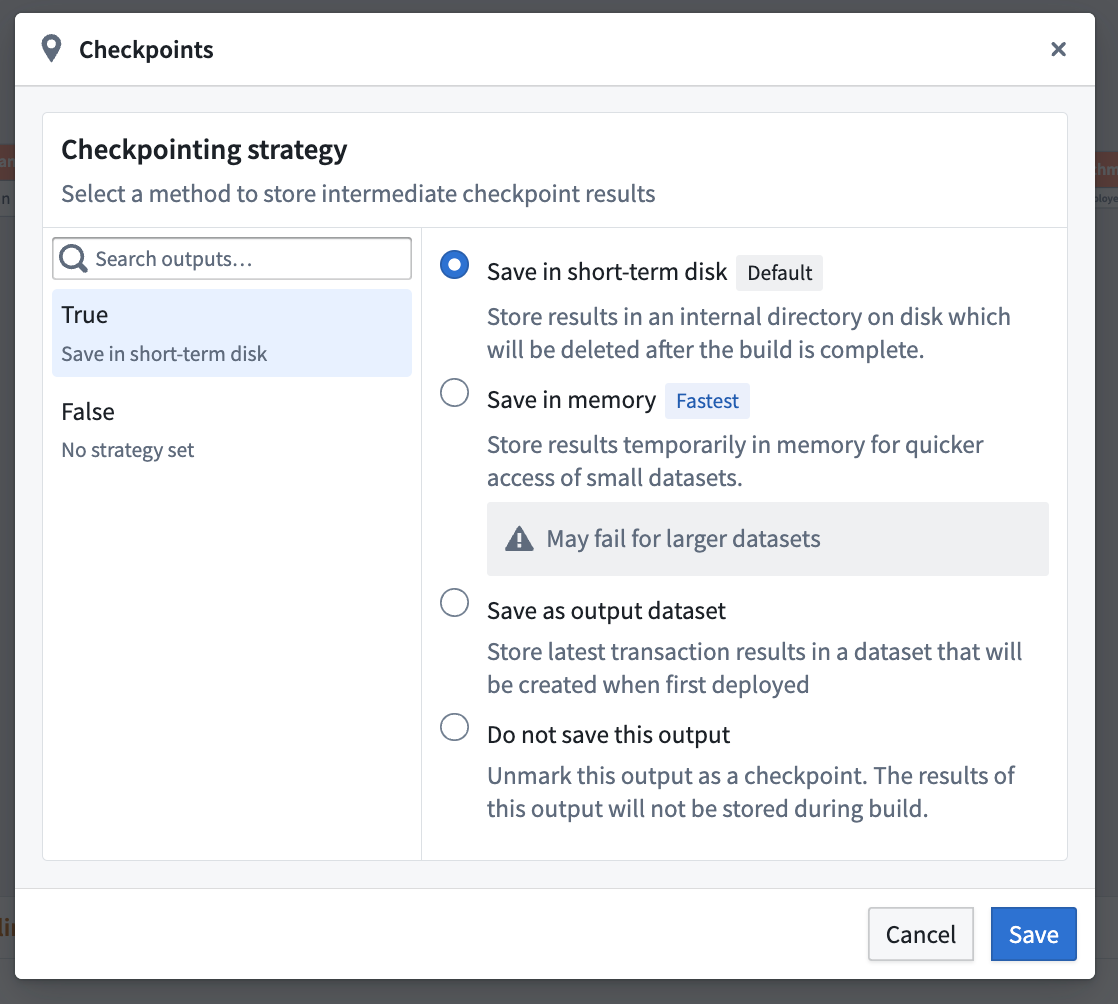
Select one of three strategies to either save in short-term disk, memory, or as output dataset.
Explore these new checkpoint options in Pipeline Builder today. Learn more about using checkpoints in Pipeline Builder.
Your feedback matters
We want to hear about your experiences with Pipeline Builder and welcome your feedback. Share your thoughts with Palantir Support channels or on our Developer Community ↗ using the pipeline-builder tag ↗.
Enforce stable version restrictions in function repositories
Date published: 2025-08-21
You can now restrict the release of stable versions of your functions by only allowing stable versions to be tagged from protected branches. This provides enhanced control over new stable version releases, ensuring that all changes being released in a stable version are required to go through code review to be merged into a protected branch first. This encourages safer practices, because new stable version releases are immediately picked up by downstream applications that are configured to automatically accept upgrades.
To enforce stable version tagging restrictions, navigate to the Protected branches setting and toggle on the Only allow stable versions to be tagged from protected branches option.
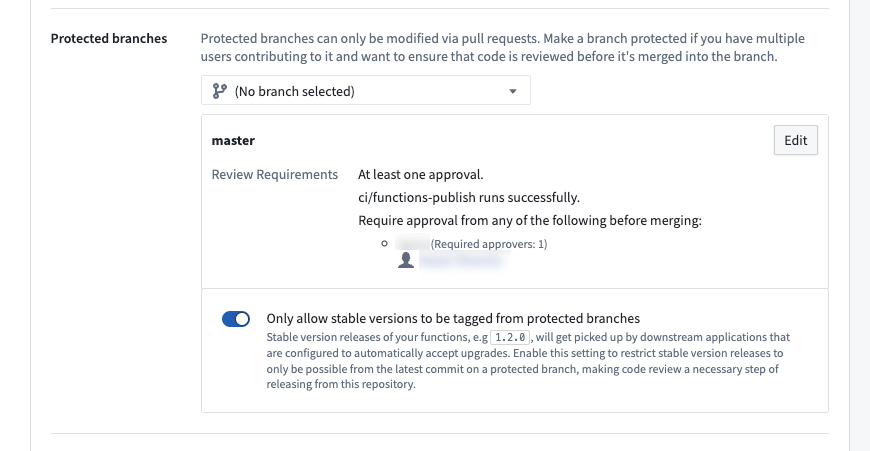
Enable stable release version restrictions in the protected branch settings.
When enabled, tagging from feature branches (non-protected branches) of the repository will block users from being able to submit a stable semantic version string. For example, 1.2.3 is a stable semantic version and is only allowed from protected branches, while 1.2.3-rc1 denotes a prerelease version that will be allowed from feature branches.
Learn more about how to protect stable function releases in the branch settings documentation.
Foundry DevOps will be generally available the first week of September
Date published: 2025-08-19
Foundry DevOps is an application for packaging and deploying data-backed workflows built in Foundry as distributable products. Package any combination of your organization's ontology, AI models, pipelines, data connections, or end-to-end use cases for seamless deployment across teams and environments. As of the first week of September, Foundry DevOps will be generally available across all enrollments and will be on by default.
Products packaged in Foundry DevOps can be distributed throughout your organization or the broader Palantir platform community via Marketplace. Through Marketplace, users can install these solutions across multiple different spaces.
Common workflows for Foundry DevOps include:
- Distributing templated solutions across multiple teams, subsidiaries, or customer environments
- Managing release cycles with automated version control and dependency management across development environments
- Building organizational ecosystems where each participant receives customized installations with their own input data
- Bootstrapping new implementations by providing proven workflows as starting points for custom use cases
Creating a Marketplace store in DevOps
The first step to using DevOps is to create a store, which holds a collection of products. DevOps stores inherit permissions from their containing projects, ensuring that anyone with edit access can create and modify products, while users with view access can install available products.
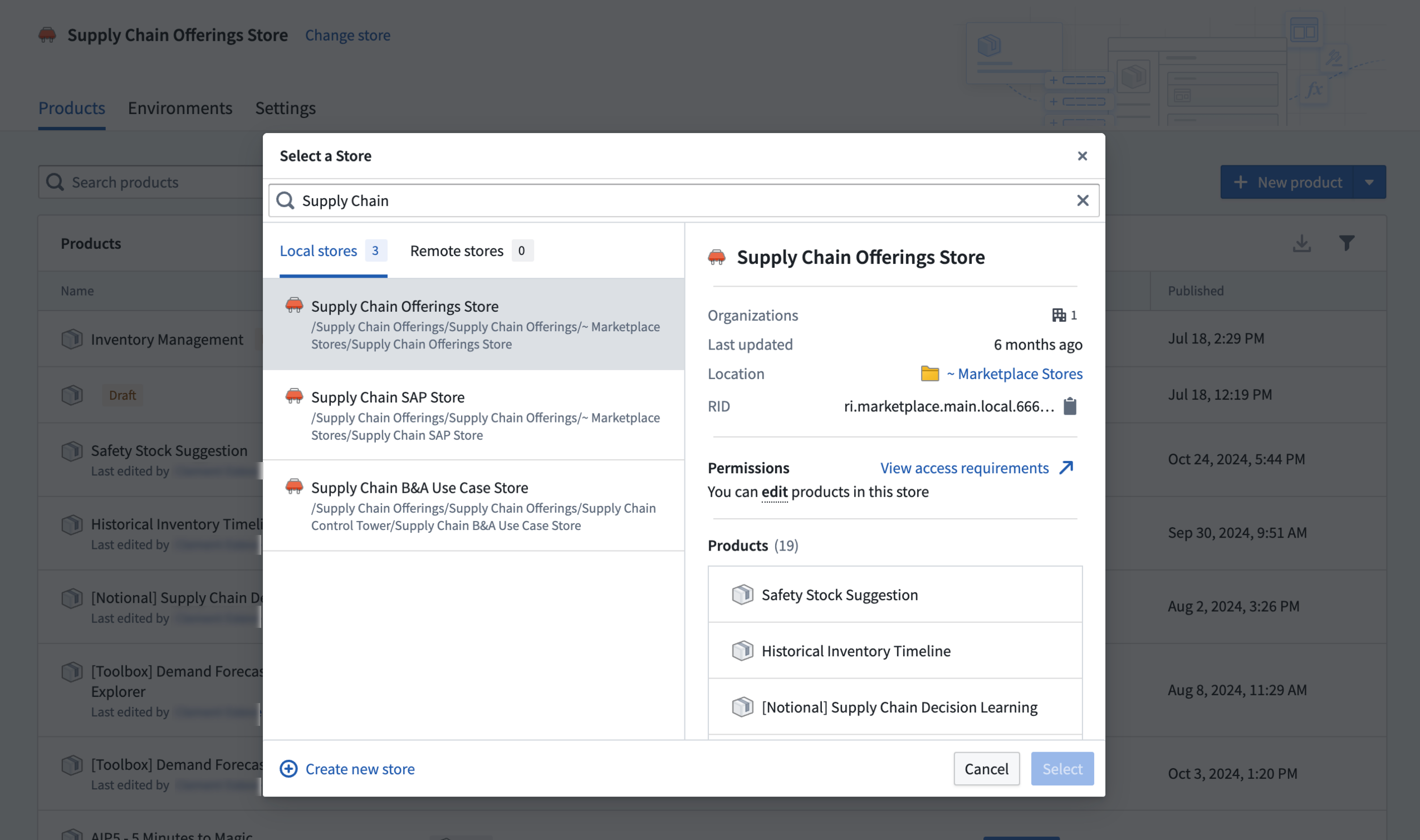
Create a Marketplace store in DevOps.
Package complex Foundry workflows in DevOps
Creating products in Foundry DevOps involves packaging your individual Foundry resources such as object types, datasets, Workshop applications, and pipelines into a comprehensive product. DevOps automatically identifies resource dependencies and allows you to iteratively build your product based on an entire workflow. Alternatively, options are provided for bulk adding all resources from a folder.
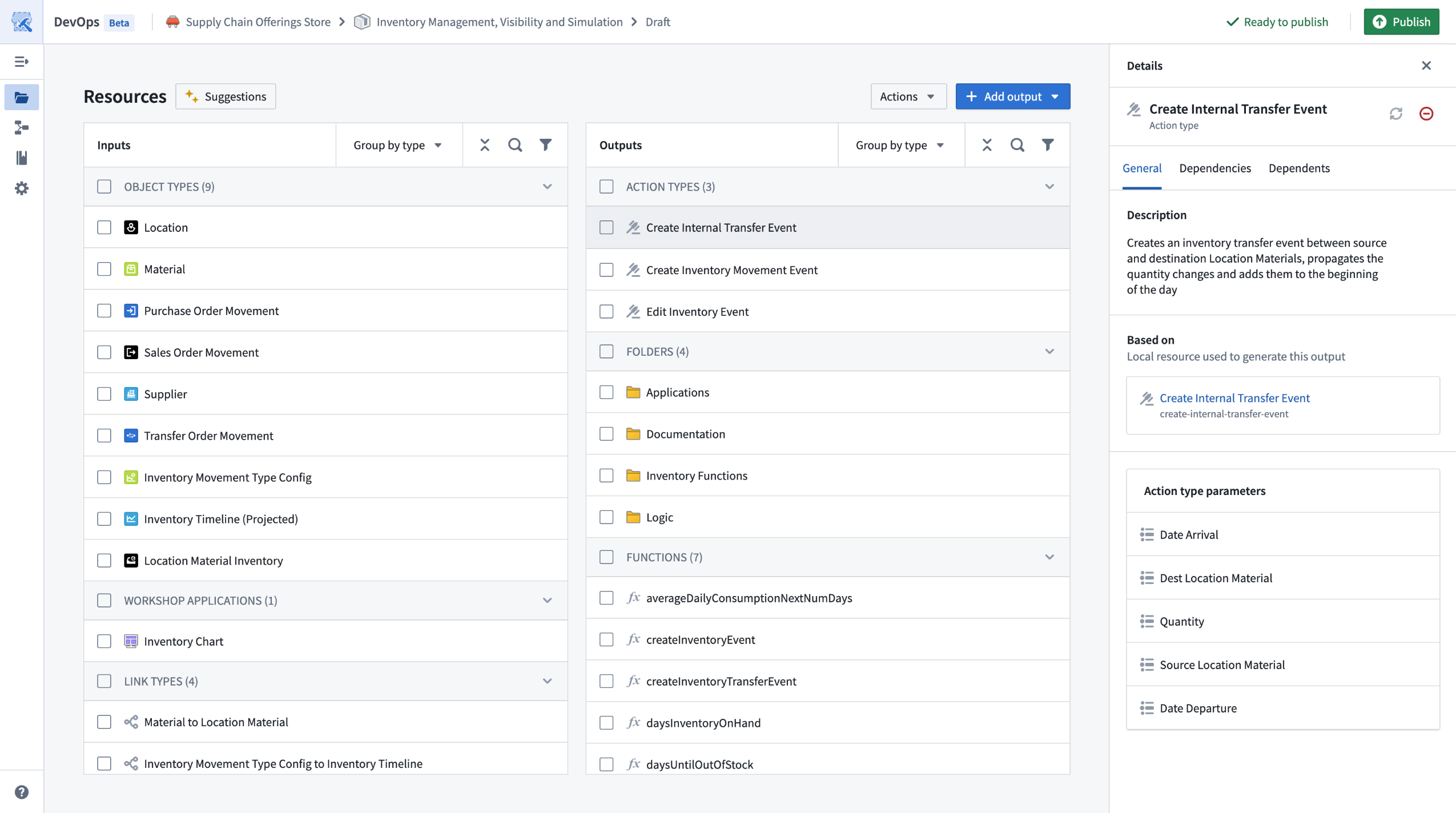
Use DevOps to package complex workflows into re-usable products.
Manage product versions and release channels
In the product overview page, you can start new versions of existing products, review previous versions, and view the latest product version for each stage of release. A preview of the latest version is shown on the product overview page.
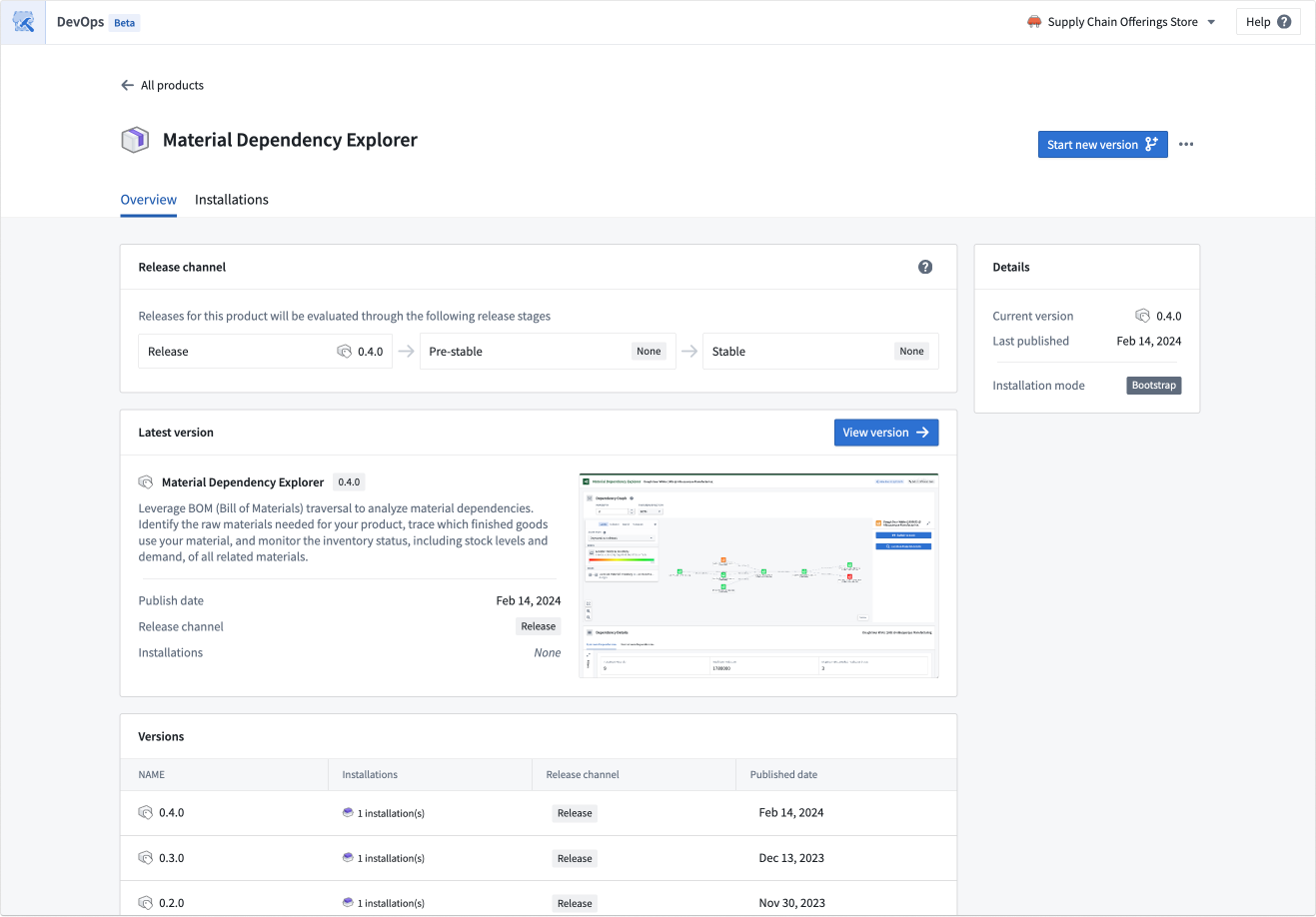
The product overview page allows you to create new versions and review previous versions.
Release management across environments
Create and manage multiple installations of your products across different environments. Release channels enable controlled rollouts, ensuring new versions only reach qualifying installations.
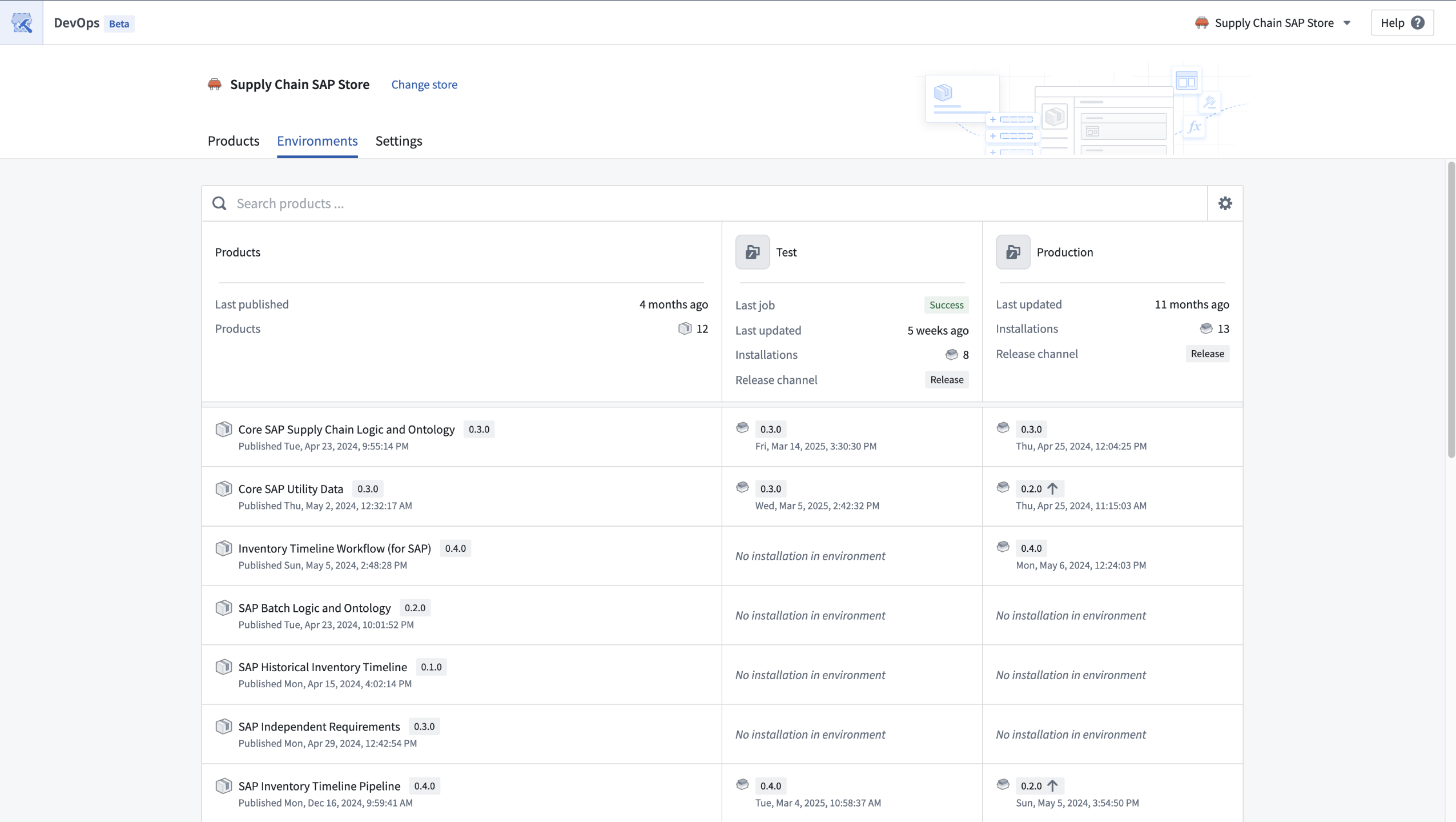
Installations of products can be managed across multiple environments.
Tell us what you think
Share your thoughts with Palantir Support, or let us know in our Developer Community ↗ forum using the devops ↗ tag.
Override per-model rate limits for projects in Resource Management
Date published: 2025-08-14
Enrollment managers are now able to configure AIP rate limits in Resource Management to override model-specific capacity allocations within a project. By manually configuring these allocations, you can set percentage-based limits for individual LLMs that override the base project limit. These overrides only apply to the projects included in that specific project limit (or for the default limit, all projects not assigned to any other manually created project limit).
The model override feature enables more granular capacity management so you can create model "allowlists". To do this, set the base project limit to 0%, add only the models you approve for use, then set an override with a specific capacity percentage. You can also explicitly disallow certain models by setting their override limit percentage to 0%.
For example, the steps below explain how to restrict projects in a project limit to only use Claude 4 Sonnet and GPT-4.1:
-
Set the base Max limit per project to 0%.
-
Add a model override for Claude 4 Sonnet at 30%.
-
Add a model override for GPT-4.1 at 25%.
-
Select Update limit to apply your changes.
Resources and users in all projects included in this project limit will only be able to access the specified models within their allocated capacity limits.
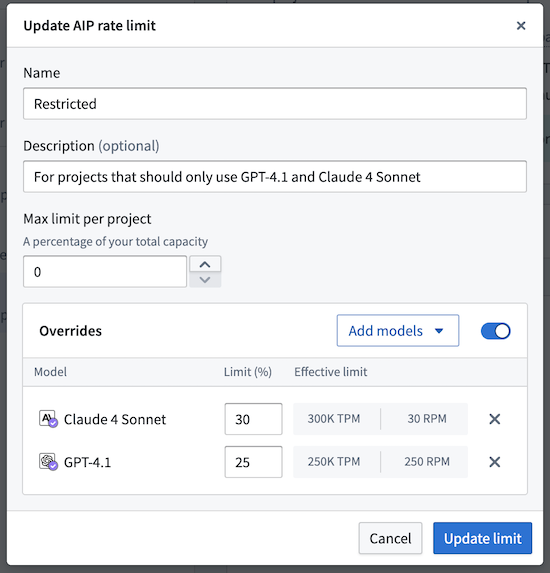
An example of an LLM rate limit override configuration for a project limit using Claude 4 Sonnet and GPT-4.1 models.
Learn more about managing LLM capacity in our documentation.
Share your thoughts
Let us know about your experience with this new feature and any feedback or questions you might have. Contact our Palantir Support channels, or create a post in our Developer Community ↗ using the language-model-service tag ↗.
Native tool calling mode now available in AIP Agent Studio
Date published: 2025-08-05
Native tool calling mode is now available in AIP Agent Studio, allowing agents to leverage built-in tool calling capabilities of supported models for improved speed and performance. Previously, agents with tools were limited to Prompted tool calling mode, which used additional prompt instructions and allowed only one tool call at a time.
You can now select the Native tool calling tool mode under the Tools settings for an AIP Agent.
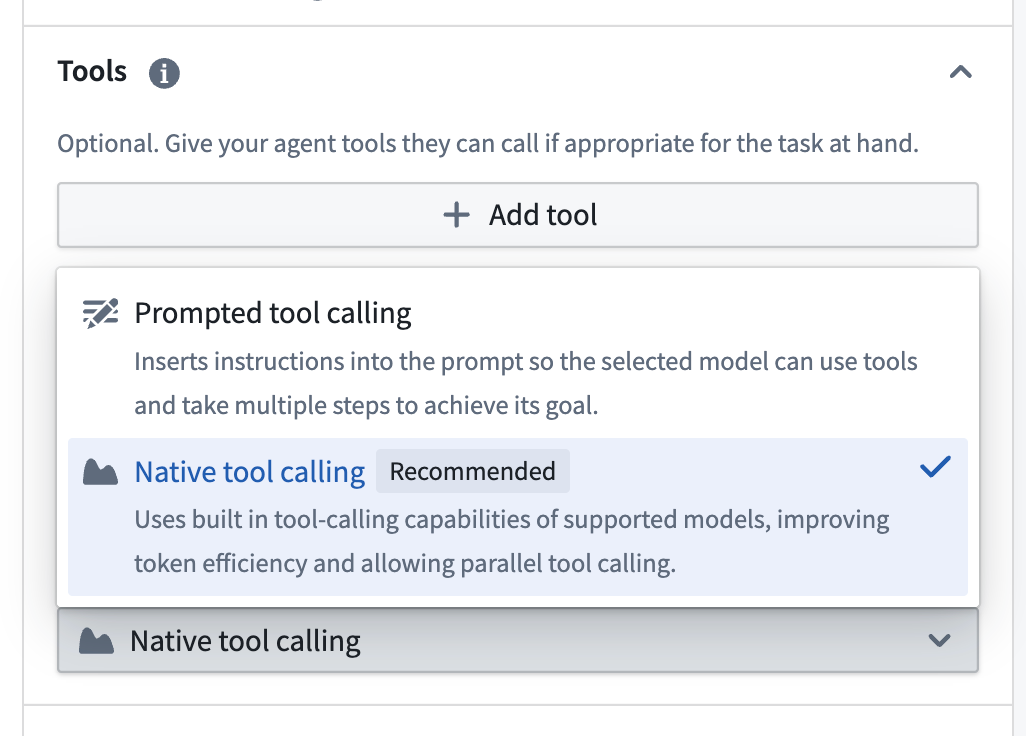
Tool settings in AIP Agent Studio with Prompted tool calling and Native tool calling tool modes available for selection.
Parallel tool call support
Native tool calling uses the built-in capabilities of supported models to improve tool calling speed and performance, offering more efficient token use and support for parallel tool calls. Parallel tool calling reduces the time required for an agent to answer complex queries that require multiple tool calls by allowing several tool calls to be made simultaneously.
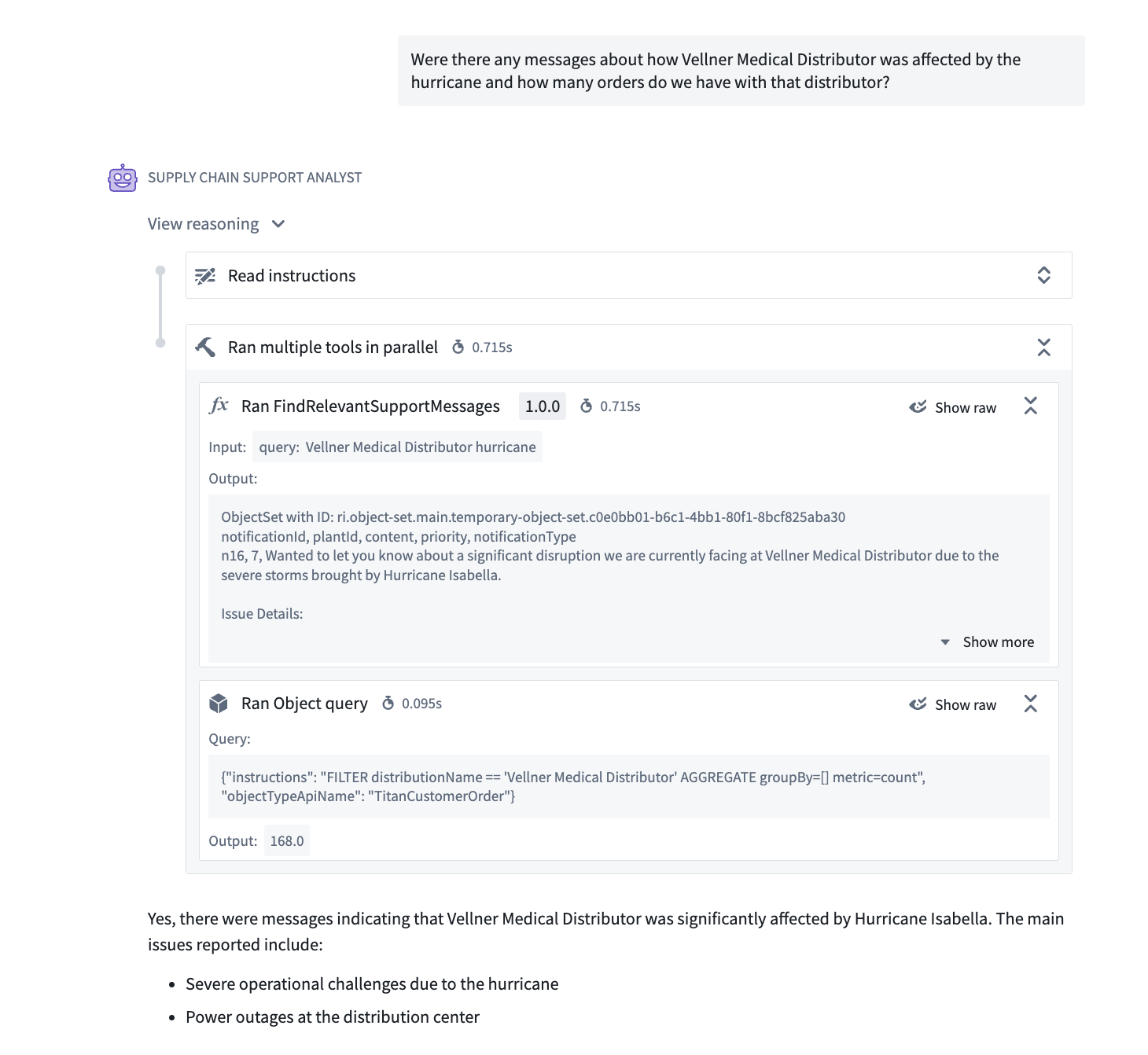
Parallel tool calls for an AIP Agent using Native tool calling mode.
Improve efficiency by reusing previous tool results
Agents in native tool calling mode can access tool calls from earlier exchanges in a conversation, enabling them to reuse previous results for more efficient responses.

A native tool calling agent reusing a previous tool result in a conversation.
Supported models and tools
Native tool calling is currently available for use with a subset of Palantir-provided models only, and with the following tools:
- Apply action
- Call function
- Object query
- Update application variable
To view the list of supported models, select Native tool calling mode under the Tools settings for your AIP Agent, then open the Model settings. For agents with unsupported models and tools at this time, continue to use Prompted tool calling mode.
For more information, review the AIP Agent Studio documentation on tools.
Your feedback matters
We want to hear about your experiences with AIP Agent Studio and welcome your feedback. Share your thoughts with Palantir Support channels or on our Developer Community ↗ using the aip-agent-studio tag ↗.
Gemini 2.5 series (Google Vertex) and Grok-4 (xAI) are now available in AIP
Date published: 2025-08-05
Gemini 2.5 Pro, Gemini 2.5 Flash, and Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite from Google Vertex are now available for general use in AIP. Gemini 2.5 Pro is Google's flagship model for complex, reasoning-heavy tasks, while Gemini 2.5 Flash provides a balance between speed, cost, and performance. Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite is the most efficient model offered. Comparisons between the Gemini 2.5 series models can be found in on Google's documentation↗.
Grok-4 is xAI's flagship model for deep reasoning and computationally intensive tasks. It offers significant improvements over Grok-3 for complex, multi-step problem solving and heavy-duty analysis, making it ideal for users who require robust logic and advanced deduction. Comparisons between Grok-4 and other models in the xAI family can be found in the xAI documentation↗.
As with all new models, use-case-specific evaluations are the best way to benchmark performance on your task.
You can use these new models in enrollments where the enrollment administrator has enabled the model family.
For a list of all the models available in AIP, review the documentation.
Additional recently models added to AIP
OpenAI (Direct or on Azure)
- GPT-4.1
- GPT-4.1 mini
- GPT-4.1 nano
- o3
- o4-mini
Amazon Bedrock
- Claude 4 Sonnet
Your feedback matters
We want to hear about your experiences using language models in the Palantir platform and welcome your feedback. Share your thoughts with Palantir Support channels or on our Developer Community ↗ using the language-model-service tag ↗.