Model functions developer guide
Model functions are automatically generated functions that wrap live model deployments, enabling models to be used for live inference in Workshop, Vertex, and other end-user applications. Model functions have the same input and output API as the underlying model and can be called from TypeScript, Python, or used directly in applications.
This developer guide covers the behavior of model functions including version updates, API changes, and configuration options. This applies to functions published from both direct model deployments and Modeling Objective live deployments.
For instructions on how to import and call model functions in your code, see Functions on models.
Before publishing a model function, ensure your model satisfies the requirements for function publishing.
Publish a model function
Model functions can be published from two types of deployments:
- Direct model deployments: From the model page, select the + icon in the sidebar after creating a direct deployment.
- You can only have one function per branch wrapping the corresponding deployment.
- Modeling Objective live deployments: From the deployment details page, use the Publish Function card after creating a live deployment to wrap it in a function.
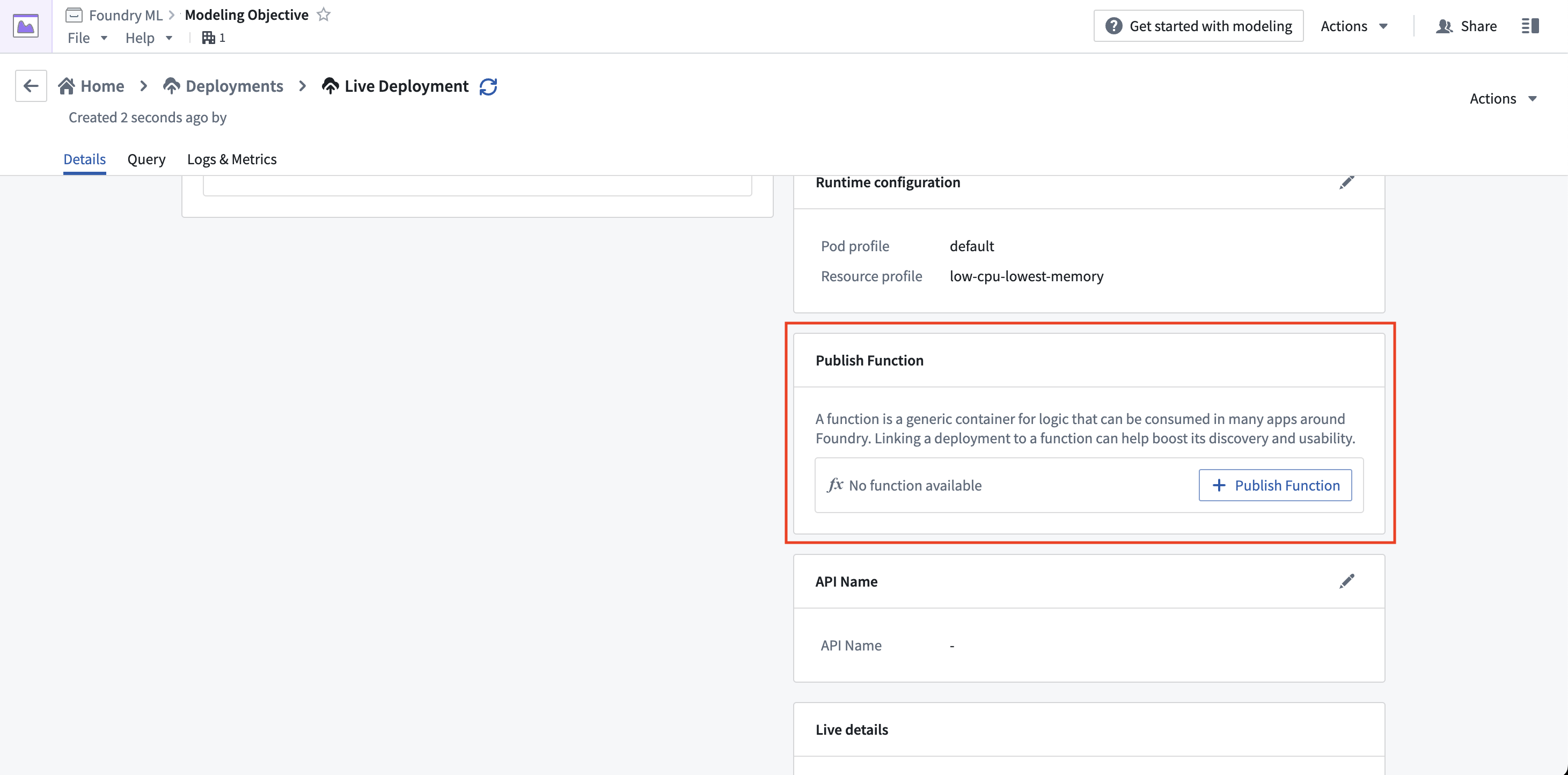
When publishing from a Modeling Objective, you will be guided through the process of setting parameters for the function.
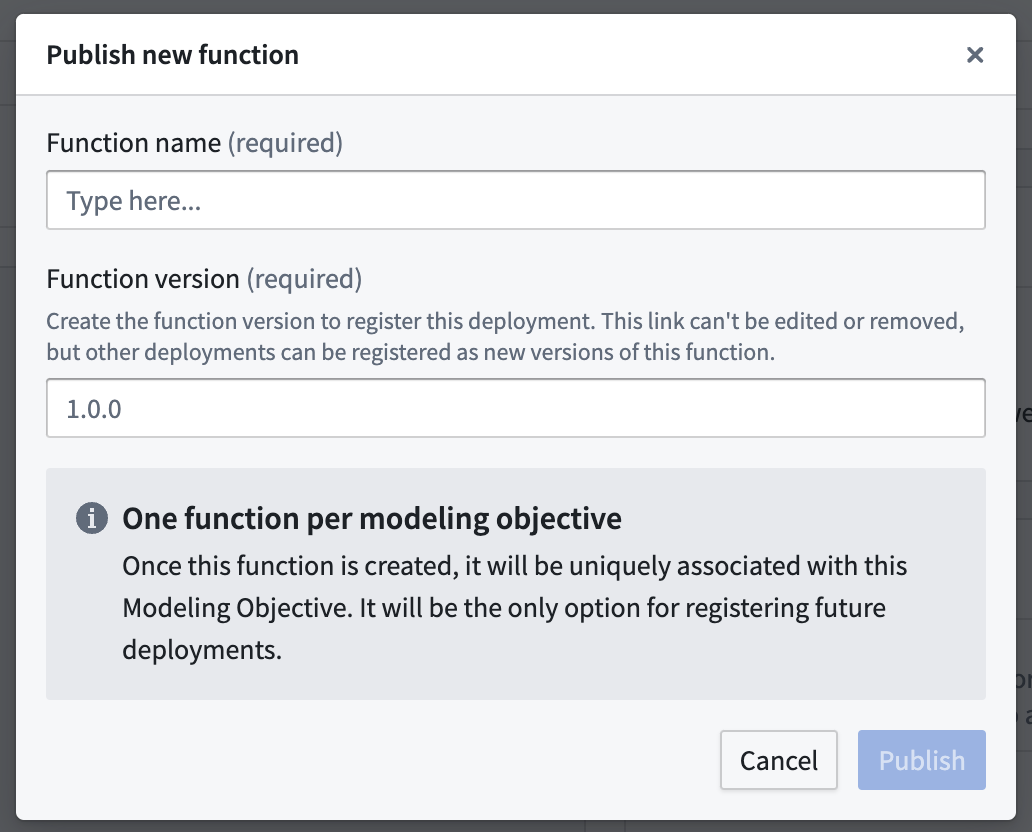
Both methods produce functionally equivalent model functions. These are simple wrappers that defer all logic to the underlying live deployment, but with the model API translated to input and outputs types recognized by functions.
To learn how to import and call model functions in your code, see Functions on models.
Function version upgrades
This section explains function upgrade behavior and how to manage consuming resources, especially in the case of Model API changes.
Direct model deployments: Automatic function version publication for each version
When a new version of the model is published on a branch with a function published, a new version of the associated function is also automatically created. It is not necessary to update consuming resources to the new function version, unless the model API has changed, as described below.
While only one function version can typically be imported in a given repository or application, users who want to import several model versions into their project for change management purposes can publish several functions on different branches to do so, since there can be one deployment and one function per branch on a model.
Modeling Objectives: Create new version after releasing if the API changed
Upon releasing a model version with an API change in Modeling Objectives, the following warning will appear in case a new function needs to be published:
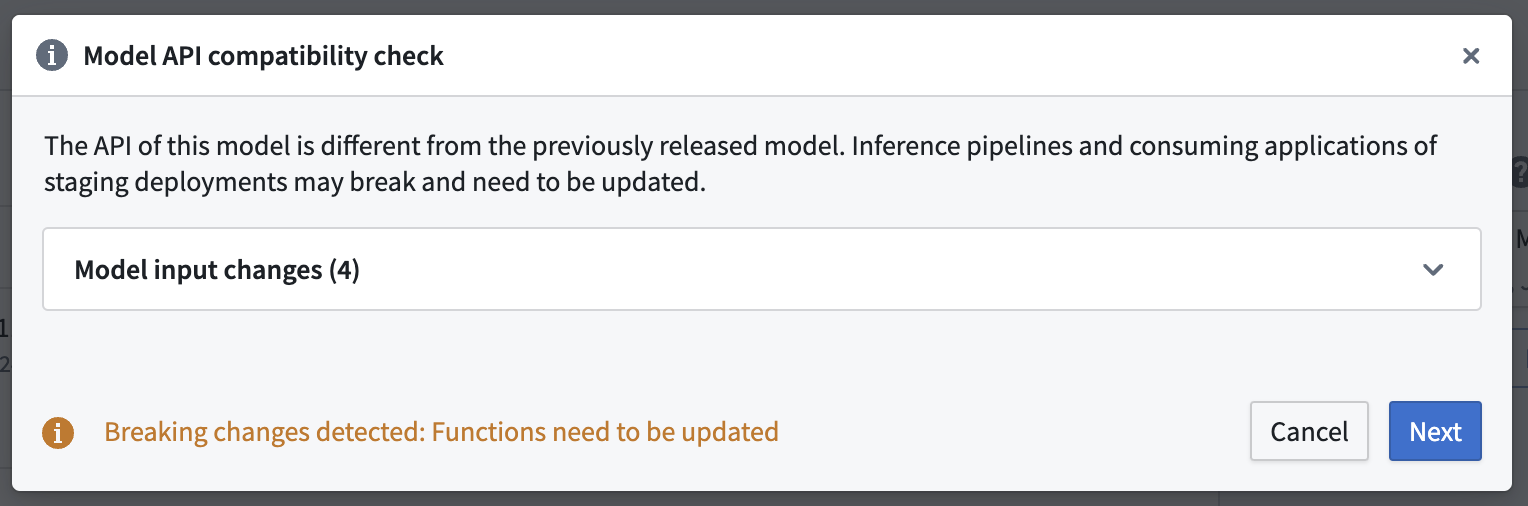
You should not ignore this warning. Updating a live deployment to a new model with a different model API will require manual action to fix downstream usage. The dialog will guide you through the process of publishing new function versions for any deployment affected by the release.
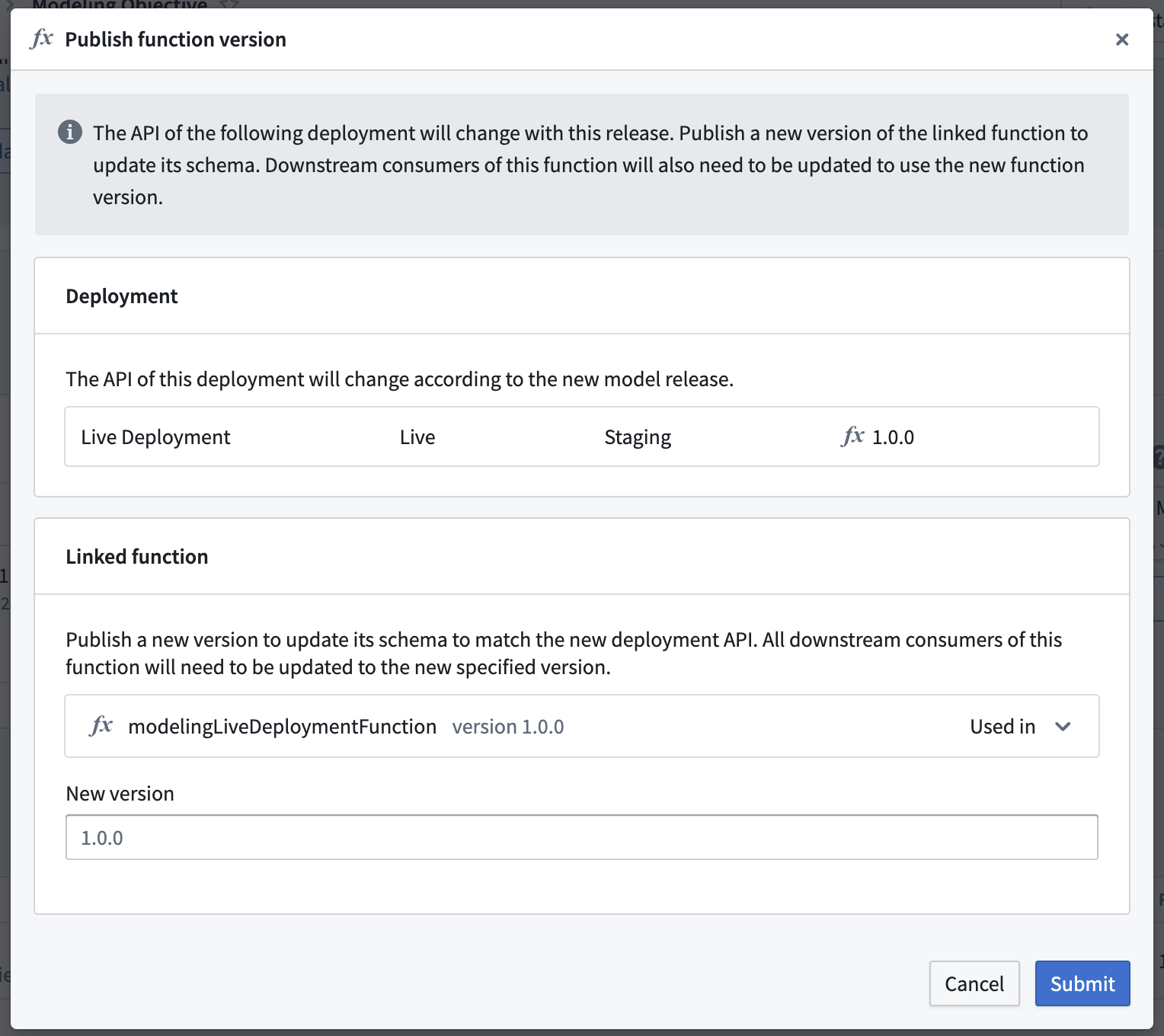
Usages of the current function version will break if you choose not to publish a new function version. To resolve this issue, return to the Details page of the deployment and publish a new function version.
Model API change
When a Model API changes between versions, consumers must be updated to continue working. This includes TypeScript v1 functions and Workshop applications. Model functions mirror your model's API using Function-supported types. After an API change:
- Previous model function versions will expose outdated APIs that no longer match the current model.
- Both functions and the underlying live deployment validate inputs/outputs against the current API.
- Previous model function versions will fail validation and stop working, as the live deployment only accepts inputs/outputs matching the new model API version.
You should update your model functions and applications after each model API change.
Upgrading a model function dependency in Code Repositories
TypeScript v1
To upgrade a model function dependency, edit the resources.json file to select the new version of the model function. This will automatically regenerate the necessary type bindings.
TypeScript v2 and Python
Simply remove and re-import the function using the Resource import sidebar, specifying the right version.
Row-wise publishing
Row-wise publishing flattens the function API for models with tabular inputs and outputs, allowing each function call to process a single row instead of an array.
For models that are single tabular input to single tabular output, row-wise function publishing will be enabled by default. This allows the model API to be flattened for each inference call so that executing the function calls one tabular row as input and outputs one tabular row. Alternatively, consider using an Object or ObjectSet directly in the Model API to facilitate use of your model with objects in functions.
For a model API that looks like the following:
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14@classmethod def api(cls): inputs = { "input_df": pm.Pandas(columns=[("area_code", int), ("num_bedrooms", int), ("num_bathrooms", int)]) } outputs = { "output_df": pm.Pandas(columns=[("area_code", int), ("num_bedrooms", int), ("num_bathrooms", int), ("predicted_price", int)]) } return inputs, outputs
The direct publishing function signature with row-wise processing would look like:
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10export async function housingPriceModelingObjective(parameters: { "area_code": FunctionsApi.Integer; "num_bedrooms": FunctionsApi.Integer; "num_bathrooms": FunctionsApi.Integer; }): Promise<{ "predicted_price": FunctionsApi.Double; "num_bathrooms": FunctionsApi.Integer; "area_code": FunctionsApi.Integer; "num_bedrooms": FunctionsApi.Integer; }>
The direct publishing function signature without row-wise processing would look like:
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14export async function housingPriceModelingObjective(parameters: { "input_df": Array<{ "num_bathrooms": FunctionsApi.Integer; "area_code": FunctionsApi.Integer; "num_bedrooms": FunctionsApi.Integer; }>; }): Promise<{ "output_df": Array<{ "predicted_price": FunctionsApi.Double; "num_bathrooms": FunctionsApi.Integer; "area_code": FunctionsApi.Integer; "num_bedrooms": FunctionsApi.Integer; }>; }>
To enable or disable row-wise processing for a given function, a new function version must be published and row-wise processing can be toggled under Advanced options.