Configure Environment settings
The Environment's Settings tab allows you to view and edit the settings for the Environment and its managed Entities.
Editing the Environment settings will create a change request. Environment editors can approve or reject the change request.
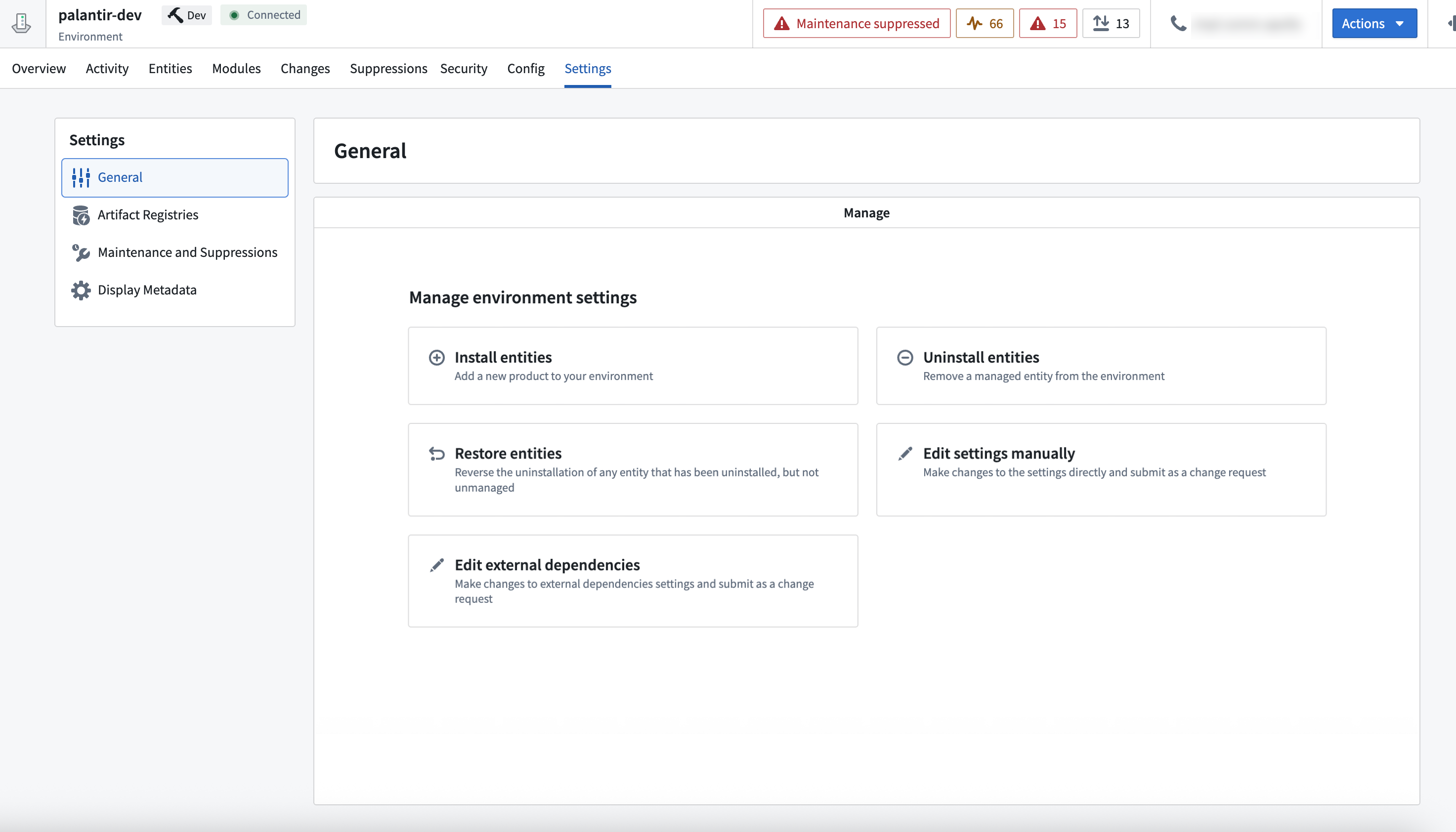
The General settings enable you to:
- Install Entities
- Uninstall Entities
- Restore Entities
- Edit external dependencies
Artifact Registries
The Artifact Registries settings allow you to assign an Artifact Registry to an Environment.
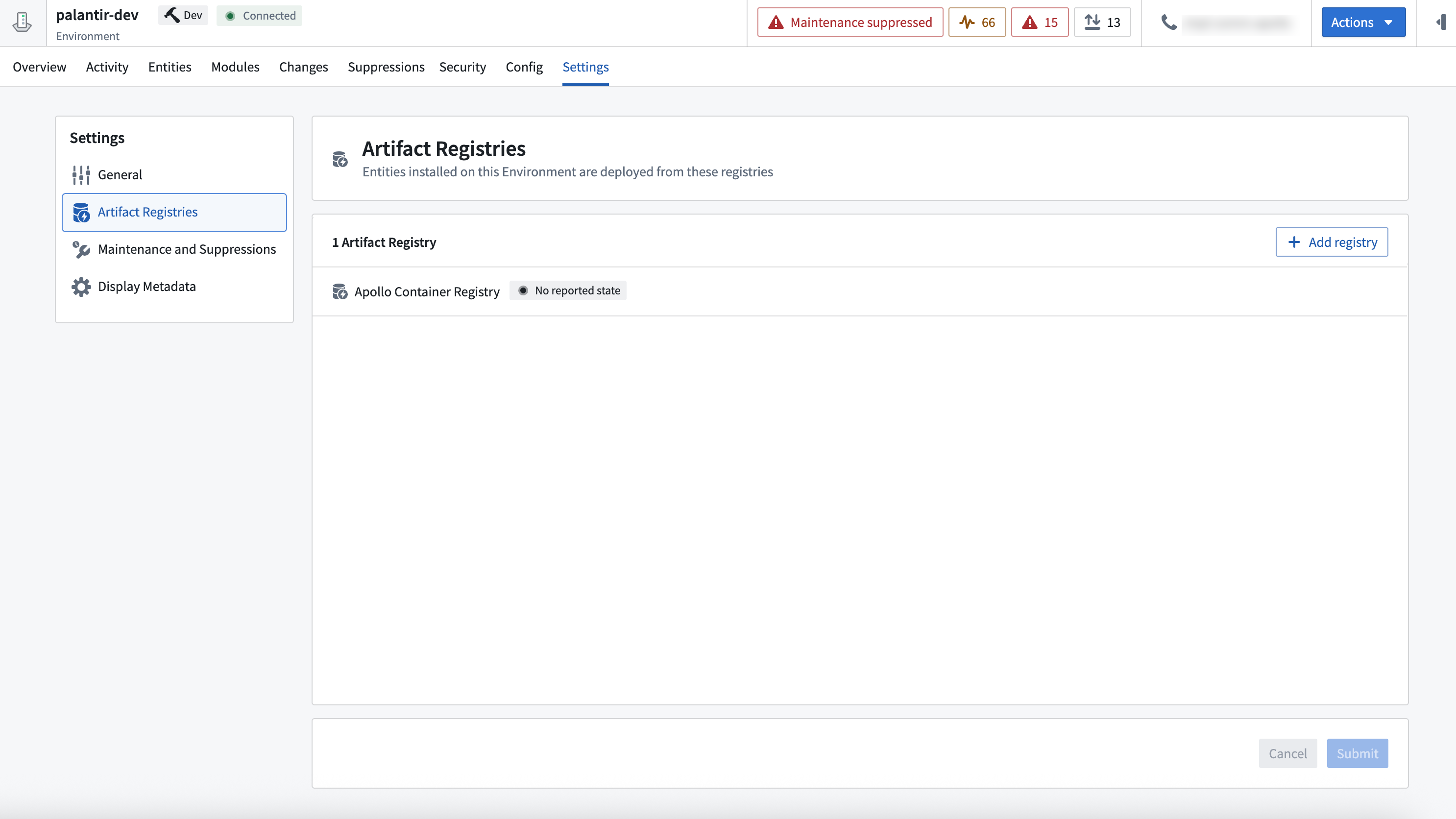
Learn more about assigning Artifact Registries.
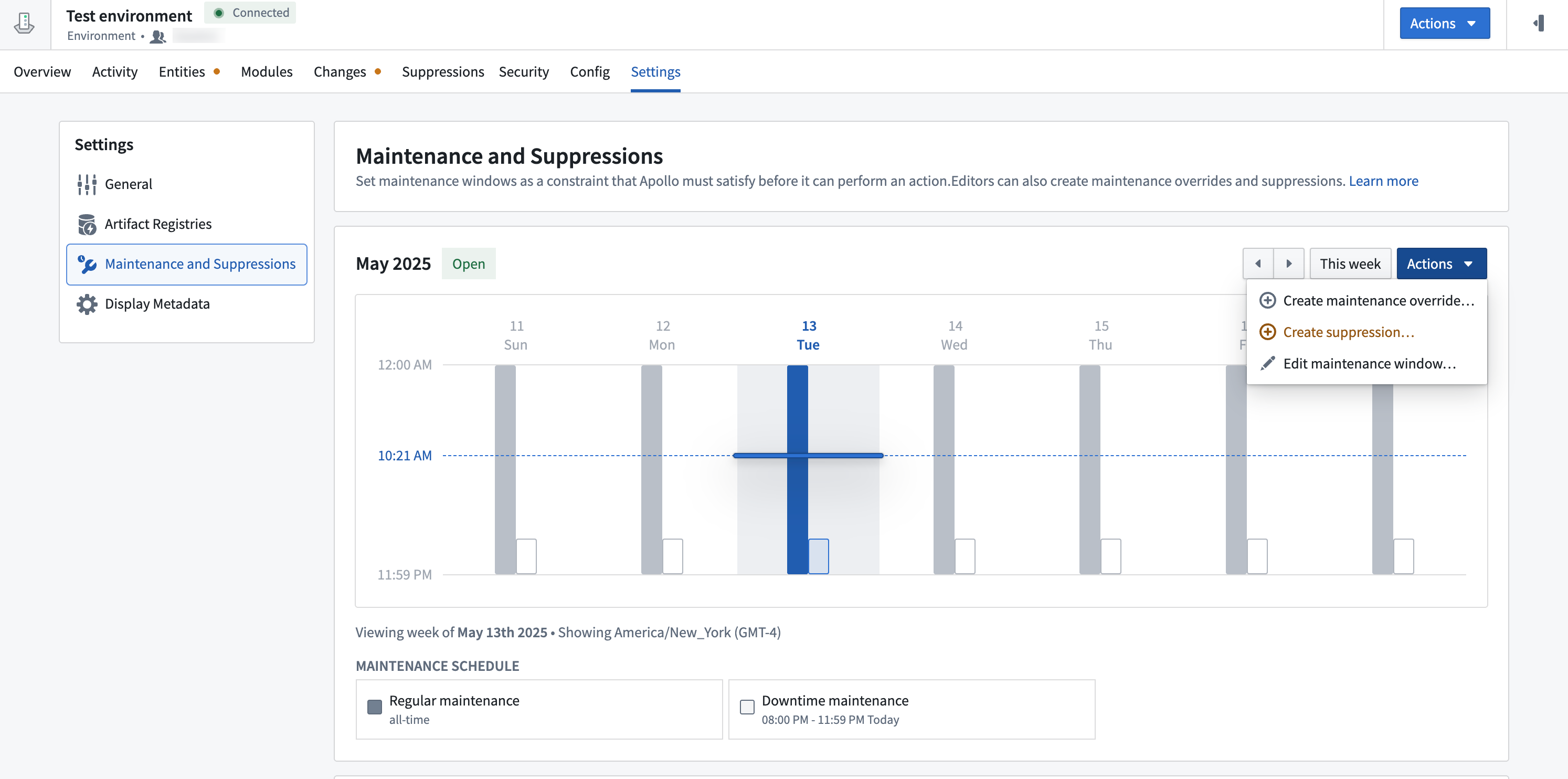
Maintenance and suppression windows
The Maintenance and Suppressions tab allows you to view and manage maintenance and suppression windows for the Environment and its Entities.
Select Actions to edit maintenance windows, create maintenance window overrides, and create suppression windows.
The Maintenance Overrides table displays the maintenance window overrides for the Environment and its Entities. The table can be filtered to overrides that are on the Environment or individual Entities, and to active or historical overrides.
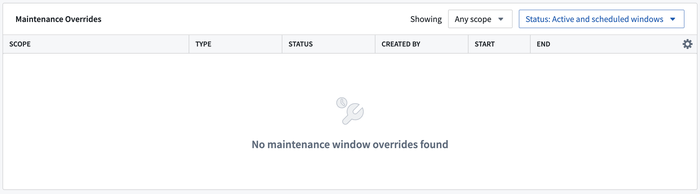
Learn more about defining maintenance window overrides.
The Suppressions table displays the active suppressions windows for the Environment and its Entities. The table can be filtered to overrides that are on the Environment or individual Entities, and to active or historical suppression windows. 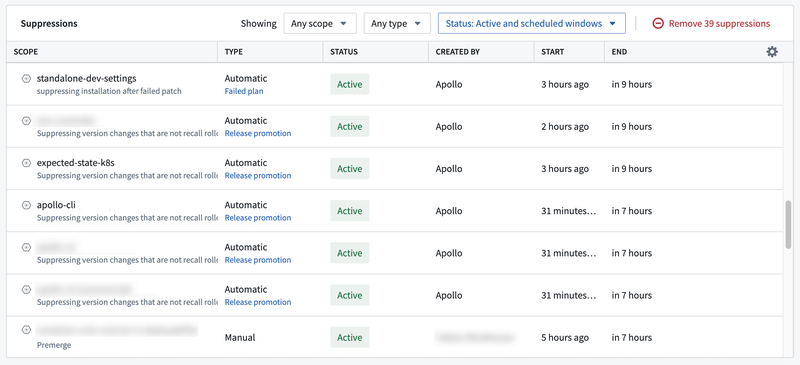
Learn more about configuring suppression windows.
Display metadata
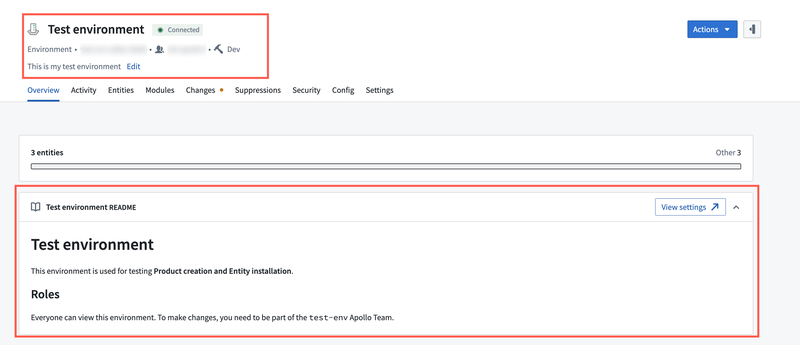
In the Display metadata tab, you can update the display name, description, and README for the Environment.
The display name will replace the Environment name in the Environment page header, as well as anywhere else in Apollo that the environment is referenced, such as dropdowns and lists.
The description should include high level information about the environment, and will be displayed under the title in the Environment page header.
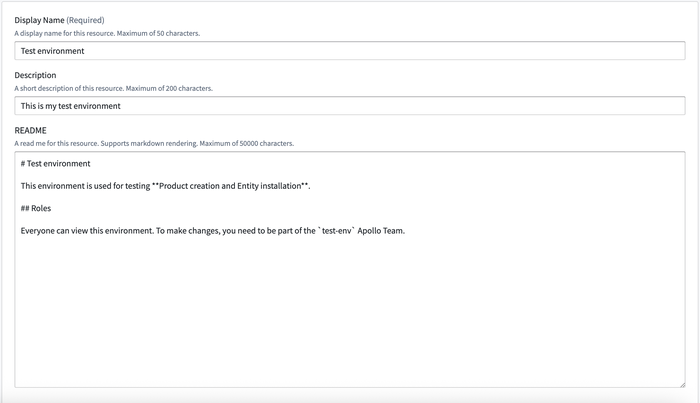
The README field should include detailed information about the Environment, such as migration plans or documentation. The README supports Markdown rendering, and will render external links, tables, lists, and more. You can view the README in the Environment Overview tab.
Edit settings manually
Apollo provides specific actions for editing the Environment settings. The actions below are not recommended and should only be used when necessary.
Select Edit settings manually to edit to directly edit the Environment settings YAML file.
Set default Release Channel
Overriding the default Release Channel for specific Entities is not recommended and should only be used when necessary.
In addition to setting the Environment's default Release Channel, you can create overrides for the Release Channels of specific Entities. To do so, add a release-channel field below the entity-locator block for the Entity. An example is shown below.
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11release-channel: RELEASE managed-helm-charts: - entity-locator: name: wordpress k8s-namespace: namespace2 product: com.bitnami.repos:wordpress - entity-locator: name: keycloak k8s-namespace: customer-namespace product: com.bitnami.repos:keycloak release-channel: DEV
In the above example the default Release Channel for the Environment is set to RELEASE. The wordpress Entity will use this default, while keycloak has an Entity-level override that subscribes it to the DEV Release Channel.
Environment and Entity maintenance windows
Environment and Entity maintenance windows are scheduled recurring time ranges during which Apollo can perform maintenance actions such as upgrading services, applying config changes, and installing new Entities within the scope of a specific Environment.
You can submit a change request to create temporary maintenance window overrides for Environments and Entities to create a non-recurring maintenance window.
Define maintenance windows
Environment editors can specify the Environment maintenance window in the Environment’s settings file under the global-maintenance-windows field.

Environment editors can also submit a change request to create overrides for specific Entities’ maintenance windows in the Environment settings file like below, by populating the maintenance-windows field below the entity-locator block for that Entity. Environment editors can also specify whether to override all Product maintenance windows for all Entities in the Environment with the field override-product-maintenance-windows: false.
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28global-maintenance-windows: downtime: all-time no-downtime: all-time maintenance-windows: schedule-a: time-intervals: - WEDNESDAY/00:00-SUNDAY/23:59 time-zone-name: US/Pacific schedule-b: time-intervals: - WEDNESDAY/19:00-WEDNESDAY/19:30 time-zone-name: US/Pacific managed-helm-charts: - entity-locator: name: wordpress k8s-namespace: namespace2 product: com.bitnami.repos:wordpress maintenance-windows: downtime: schedule-a no-downtime: schedule-b - entity-locator: name: keycloak k8s-namespace: customer-namespace product: com.bitnami.repos:keycloak release-channel: DEV maintenance-windows: downtime: all-time no-downtime: schedule-b
Entity resolved maintenance window
An Entity resolved maintenance window is the window which will be used for maintenance window constraint evaluation. Apollo will calculate the resolved maintenance window for each Entity in an Environment based on the Entity's declared maintenance window and the Product's maintenance window.
Maintenance windows: No-downtime vs. downtime
Apollo offers two types of maintenance windows:
- Downtime maintenance windows: Allow for changes where all the nodes on that Entity may go offline
- No-downtime maintenance windows: Allow for changes that will not cause any visible downtime for end users
Changes that do not require downtime can still be performed during downtime maintenance windows, but not vice versa; changes that require downtime cannot be performed outside of downtime maintenance windows.
(Optional) Override Product maintenance windows
Optional flag to disable Product maintenance windows. When enabled, Apollo will disregard the Product's maintenance window and only consider the Environment's maintenance window. The default value is false. Example:
override-product-maintenance-windows: true
(Optional) Require maintenance windows for no-downtime recalled Release roll-offs
Apollo’s default behavior is to roll off recalled Releases that do not require downtime outside of maintenance windows. You can use the following optional flag to opt out all Products on a Environment from Apollo’s default recall behavior. Defaults to false. Example:
require-maintenance-windows-for-no-downtime-recalled-release-roll-offs: true
It is strongly recommended that this flag is not overridden to ensure there are no delays to recalls of problematic Releases. This flag should only be overridden to true in cases when there are strong reason for it.
Ignored dependencies
Environment editors can override Product dependency constraints for an Entity by adding ignored dependencies. To do so, add an ignored-dependencies field below the entity-locator block for the Entity. You can list multiple Products in this field. An example is shown below.
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8managed-helm-charts: - entity-locator: name: wordpress k8s-namespace: namespace2 product: com.bitnami.repos:wordpress ignored-dependencies: - com.bitnami.repos:nginx - com.bitnami.repos:mariadb
Dependency groups
Environment editors can create dependency groups to organize Entities into logical groupings.
When dependency groups are configured:
- An Entity will only consider a Product Release dependency satisfied if the Entity shares at least one group with the dependent Entity
- An Entity will only consider a Product Release incompatibility active if the Entity shares at least one group with the target Entity
Example use case
Consider a scenario where you have a dependency relationship A -> B, meaning A depends on B. You want to run two separate instances of these Products simultaneously: A1 and A2, where A1 depends on B1 and A2 depends on B2.
Initially, you have A1 and B1 installed and working together. Now you want to install A2, but you need it to depend on B2 rather than the existing B1.
With dependency groups, you can achieve this isolation by:
- Placing A1 and B1 in the same dependency group (e.g.,
production) - Placing A2 in a separate dependency group (e.g.,
staging)
This configuration ensures that when you install A2, its dependency on B is not satisfied by the existing B1 instance. Instead, A2 will wait for B2 to be installed in the same dependency group before proceeding.
Configure dependency groups
To configure dependency groups for an Entity, add a dependency-groups field below the entity-locator block. You can specify multiple groups for a single Entity.
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13managed-helm-charts: - entity-locator: name: wordpress k8s-namespace: namespace product: com.bitnami.repos:wordpress dependency-groups: - group-1 - entity-locator: name: mariadb k8s-namespace: namespace product: com.bitnami.repos:mariadb dependency-groups: - group-1
Override dependency group behavior
You can override the default dependency group behavior for specific dependencies using dependency-group-overrides. This allows you to specify which groups to search when resolving dependencies for particular Products.
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11managed-helm-charts: - entity-locator: name: wordpress k8s-namespace: namespace product: com.bitnami.repos:wordpress dependency-groups: - group-1 dependency-group-overrides: com.bitnami.repos:shared-database: - default - shared-services
Wildcard overrides
Use the wildcard "*" to allow an Entity to satisfy dependencies from any group:
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10managed-helm-charts: - entity-locator: name: shared-service k8s-namespace: shared product: com.example:shared-service dependency-groups: - shared-services dependency-group-overrides: com.example:monitoring: - "*"
Default behavior
- No groups specified: Entities without explicit
dependency-groupsare assigned to thedefaultgroup. - Empty groups: An empty
dependency-groupslist is treated as["default"]. - No overrides: Dependencies are resolved within the Entity's own groups when no overrides are specified.