- Capabilities
- Getting started
- Architecture center
- Platform updates
Language models within functions
Palantir provides a set of language models which can be used within functions. Read more about Palantir-provided LLMs.
To use Palantir-provided language models, AIP must first be enabled on your enrollment. You must also have permissions to use AIP builder capabilities.
Palantir provides a set of language models which can be used within functions. Read more about Palantir-provided LLMs.
Import a language model
To begin using a language model, you must import the specific model into the code repository where you are writing your functions by following the steps below:
- Navigate and open the Model Imports side panel to see all existing imported models.
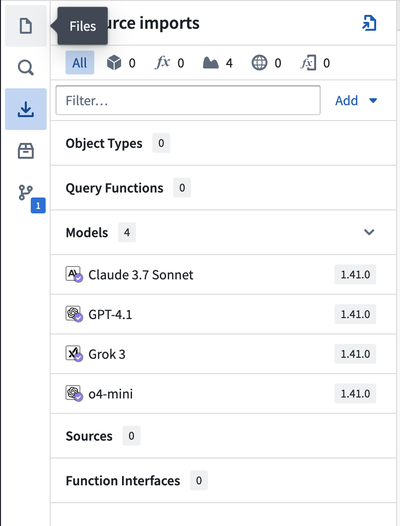
- To import a new language model, select Add in the upper right corner of the Resource Imports panel, then select Models. This will open a new window where you will be able to see Palantir-provided models that are available to you.
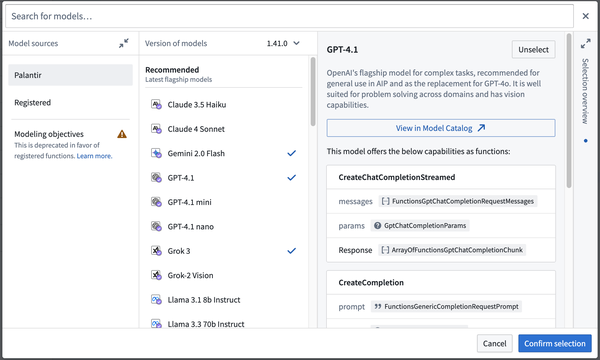
-
You will also see a tab where you can view custom models created through the Modeling Objectives application or direct model deployments previously. More information on using those models can be found in the functions on models documentation.
-
Choose the models you would like to import, then select Confirm selection to import these models into your repository. Task runner will execute the
localDevtask, generating code bindings to interact with these models. -
After importing the language models, select the model in the sidebar to view the detailed capabilities offered by this model. You can also copy code snippets to help you import and author functions with the model.
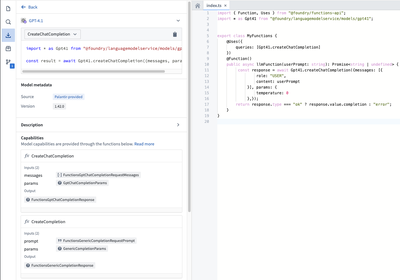
Write a function that uses a language model
At this stage, you can now write a function that uses the language model you imported. For this example, assume that you imported GPT-4.1.
Begin by adding the following import statement to your file:
Copied!1 2import { Function } from "@foundry/functions-api"; import { Gpt41 } from "@foundry/languagemodelservice/models";
Each language model will have generated methods available with strongly typed inputs and outputs. For example, the GPT-4.1 model provides createChatCompletion, createChatVisionCompletion, and createChatCompletionStreamed as different APIs to interact with the model. The list of capabilities could expand in later versions of the imported model.
In the following illustrative example, the provided GPT_4o model is used to run a simple sentiment analysis on a piece of text or image provided by a user. The function will classify the text as "Good", "Bad", or "Uncertain".
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55const SYSTEM_PROMPT = "Provide an estimation of the sentiment the text the user has provided. \ You may respond with either Good, Bad, or Uncertain. Only choose Good or Bad if you are overwhelmingly \ sure that the text is either good or bad. If the text is neutral, or you are unable to determine, choose Uncertain."; export class MyFunctions { @Function() public async llmFunction_createChatCompletion(userPrompt: string): Promise<string | undefined> { const response = await Gpt41.createChatCompletion({ messages: [ { role: "SYSTEM", content: SYSTEM_PROMPT, }, { role: "USER", content: userPrompt, }, ], params: { temperature: 0, }, }); return response.type === "ok" ? response.value.completion : "error"; } @Function() public async llmFunction_createChatVisionCompletion( userPrompt: string, pngBase64String: string, ): Promise<string | undefined> { const response = await Gpt41.createChatVisionCompletion({ messages: [ { role: "USER", content: [ { type: "text", text: userPrompt }, { type: "genericMedia", genericMedia: { mimeType: "IMAGE_PNG", // Base64 encoded PNG String content: pngBase64String, }, }, ], }, ], params: { temperature: 0, }, }); return response.type === "ok" ? response.value.completion : "error"; } }
This function can then be used throughout the platform.
Embeddings
Along with generative language models, Palantir also provides models that can be used to generate embeddings. A simple example is as follows:
Copied!1 2 3 4 5@Function() public async llmFunction_embeddings(inputs: string[]): Promise<Double[][]> { const response = await Textembedding3large.createEmbeddings({ inputs }); return response.type === "ok" ? response.value.embeddings : [[]]; }
This is most commonly used to perform semantic search workflows.
Upgrade from legacy language models within functions
Skip this step if you are starting from a new repository with no legacy language models imported.
The following process will result in a compile-time break in your code repository, as the code syntax will be updated. Refer to the code snippets in the sidebar for each updated model to update your code.
The updated language models in functions offer more advanced capabilities, such as better support for vision and streaming. We highly recommend upgrading your repository to take advantage of the latest AIP offerings.
- If you have existing legacy language models imported, a warning icon to upgrade will appear in the sidebar. Choose Select imports to open the model import dialog.
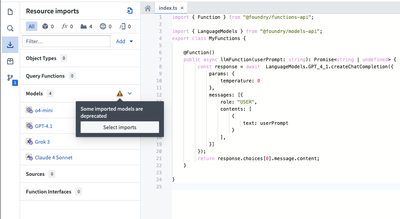
- In the model import dialog, select Fix to remove any deprecated legacy language models.
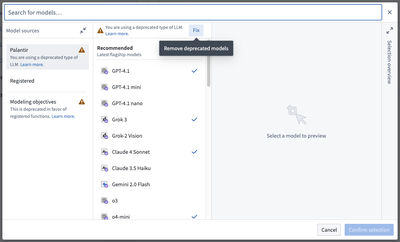
- Reselect the models to migrate to the updated language model versions. You can view additional capabilities supported by this version in the details panel in the center of the dialog.
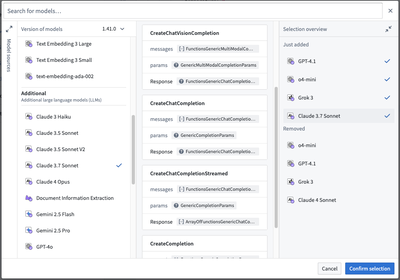
- Now, you can view the updated model imports in the sidebar. Selecting a model will show you a details panel with code snippets to help you update your code to take advantage of the additional capabilities.

Performance considerations
Certain models may have rate limits applied, limiting the number of tokens that may be passed over a certain time period. This will be enforced along with any standard limits that apply to functions.
Note: AIP feature availability is subject to change and may differ between customers.