- Capabilities
- Getting started
- Architecture center
- Platform updates
Getting started
To get started, create an Autopilot workbench from one of the following entry points:
- Directly in Autopilot: Open Autopilot from the application portal and select object types, optionally selecting the related automations to import, or select automations directly.
- From an automation: Right click an automation in a Compass folder and select Open in Autopilot. On the overview page for an automation, select Open in Autopilot in the Actions menu.
Set up your Autopilot workbench
Autopilot automatically generates an initial workbench for you based on the starting object types or automations you have selected. Top-level alerts will guide you through how to configure your workbench for a complete system view.
Configuration
- Review and add automations: When you open your workbench, Autopilot will alert you to automations related to your workflow that are not yet included in your workbench. Follow the prompts to add relevant automations for a complete system view.
- Customize kanban columns: Autopilot infers and automatically generates kanban columns, or states, based on automations in your workbench.
- Column names are generated automatically and can be edited in the settings menu in the top right of each column.
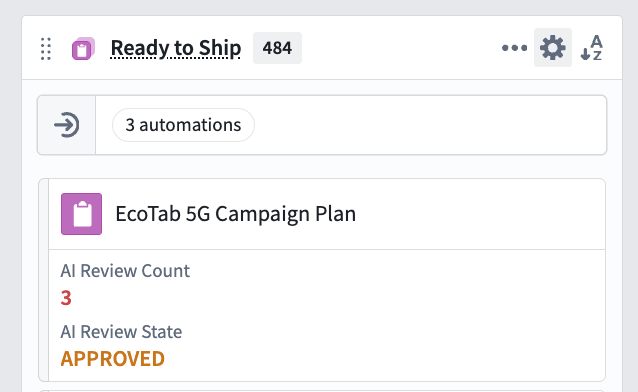
- You can also add and manually define your own columns.
- In the States sidebar, you can configure your states and drag states to reorganize the ordering in the kanban board.
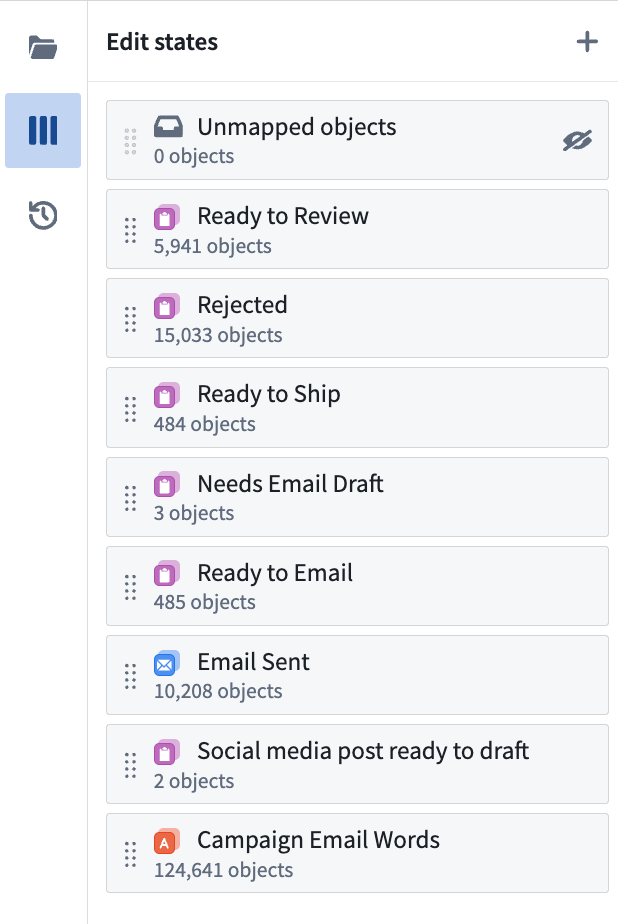
- Column names are generated automatically and can be edited in the settings menu in the top right of each column.
- Enable project-scoped mode for full visibility: For the most comprehensive view of your automation system, enable project-scoped mode on your automations. This setting allows all workbench users to see automation execution events and discover dependencies between automations.
Project-scoped mode expands permissions so that automation relationships are visible to all users in the project. Autopilot cannot infer relationships for user-scoped automations owned by another user.
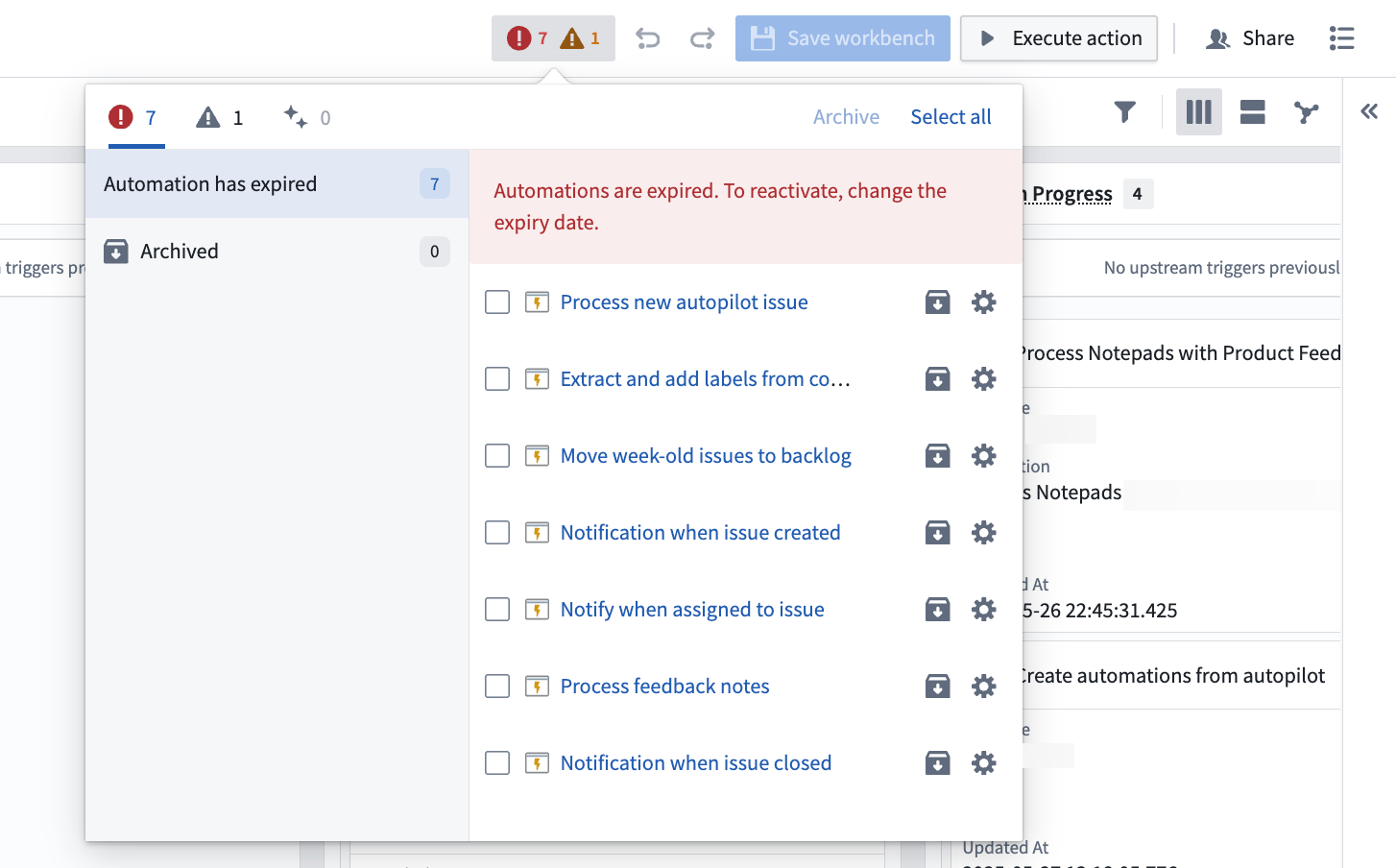
- Enable edit history tracking for object types: Enable edit history for your object types to track changes and view detailed object histories within Autopilot.
- Ensure automations have run at least once: Autopilot relies on historical executions to discover relationships between automations; if an automation has never run, Autopilot cannot infer the downstream and upstream automations in a process.
- Enable trace logs per resource: Trace logs show detailed execution for each automation run. Contact your enrollment administrator to enable logs.
For more granular logs, consider using console in your TypeScript functions or import logging in your Python functions.
- Configure object card properties and object previews: Define which object properties appear on kanban cards, set conditional formatting for properties, and customize object views in Ontology Manager. Autopilot will render the panel object view for an object in the sidebar, when available.
Embed in Workshop
Autopilot resources can be embedded into Workshop applications using an iframe. To do so, append your Autopilot URL with the query parameter ?embedded=true, or &embedded=true if you already have a ? condition in your string query. You can choose to embed the Kanban board, graph, or split view.