Function-backed time series
Function-backed time series are in the beta phase of development and may not be available on your enrollment. Functionality may change during active development. Contact Palantir Support to request access to Function-backed time series.
Function-backed time series enable you to generate and transform numeric time series using Python logic defined in a function. Foundry treats the function's output as a time series without the need to define a time series sync.
Capabilities
- Custom analytics: Write Python functions that generate numeric time series. Use any libraries, such as statsmodels or Prophet, or use proprietary code to perform advanced analytics.
- Direct integration in Foundry: Leverage function outputs directly in Quiver and apply operations such as resampling, formulas, joins, and time series search while ensuring compatibility and composability.
- On-demand data access: Easily incorporate data from external APIs or services without pre-materializing data to enable rapid prototyping and dynamic analysis.
- Parameterized scenarios: Pass custom inputs such as control settings or forecast horizons to compare multiple generated series side by side.
- Scalable production workflow: Benefit from built-in result caching and streaming execution for handling large outputs while keeping interactions responsive.
In the example below, a function-backed time series is used in a Workshop module to compute weekly forecasts in real-time. An operator is able to simulate different scenarios for how changing a machine's controls affects the predicted performance forecast.
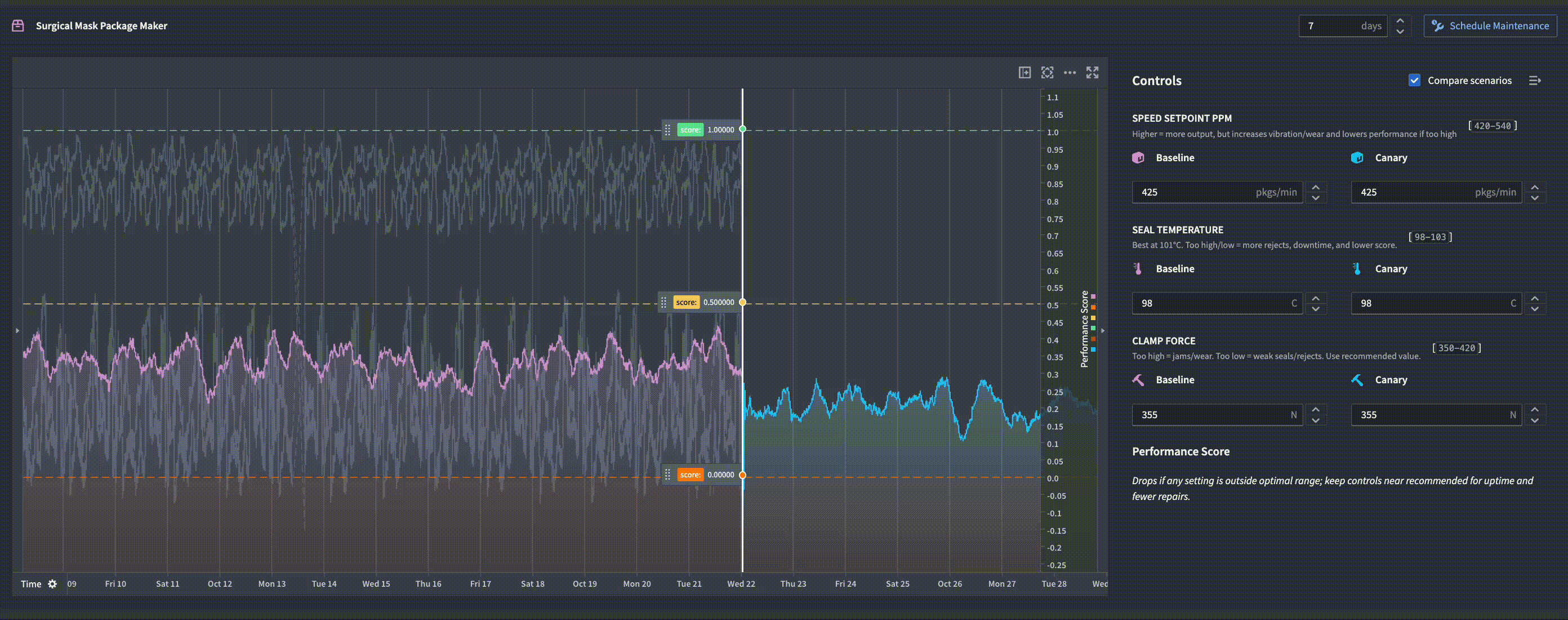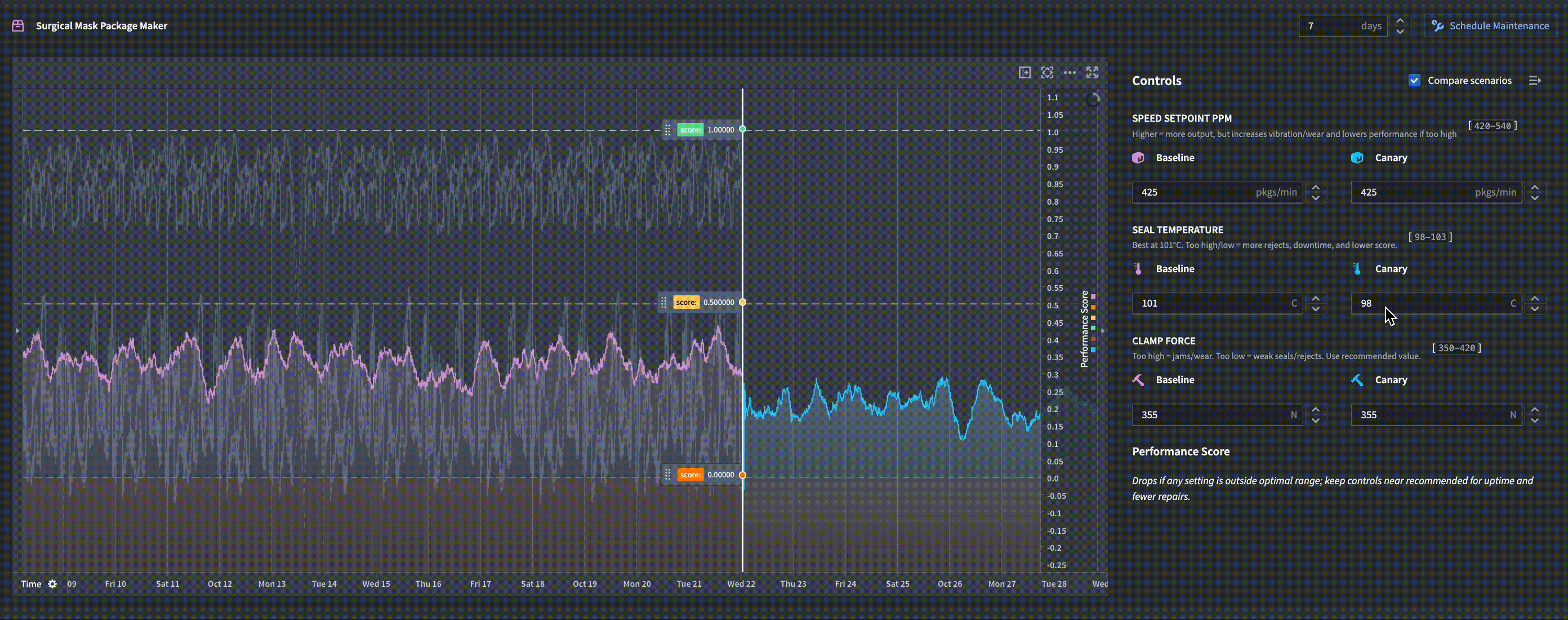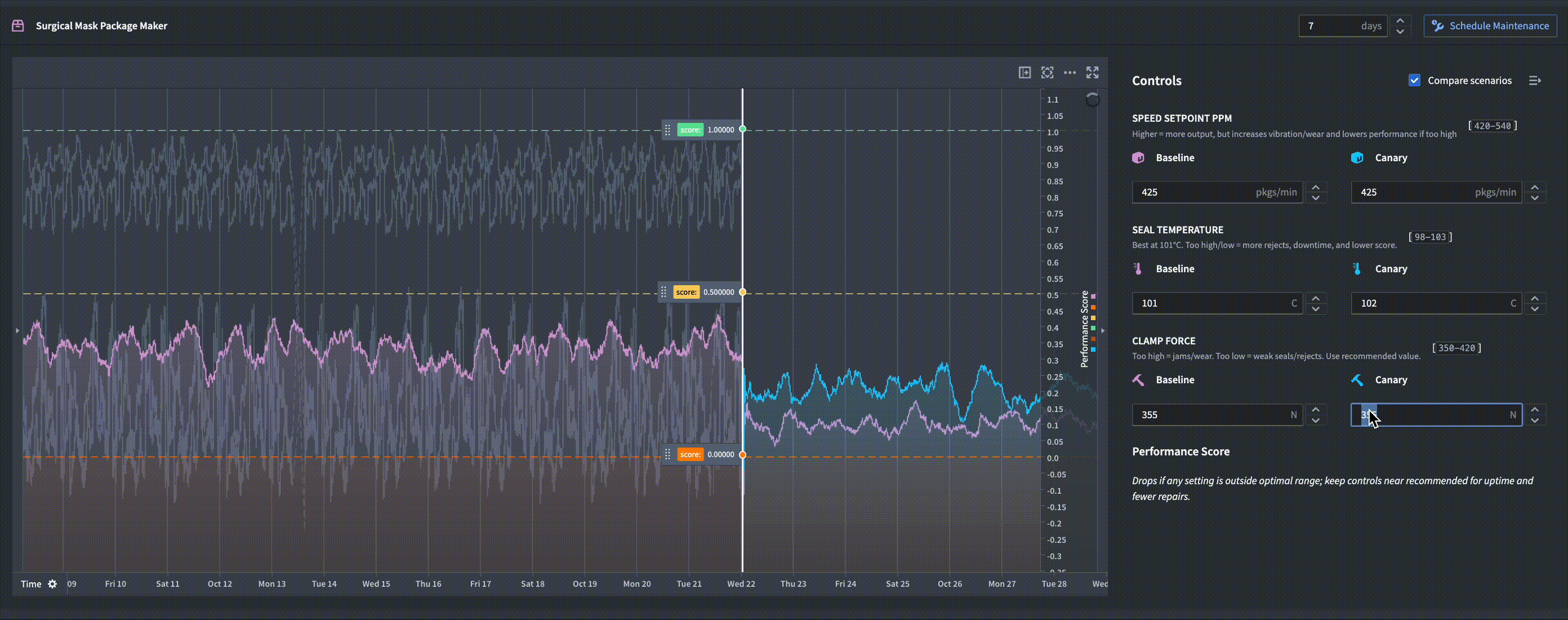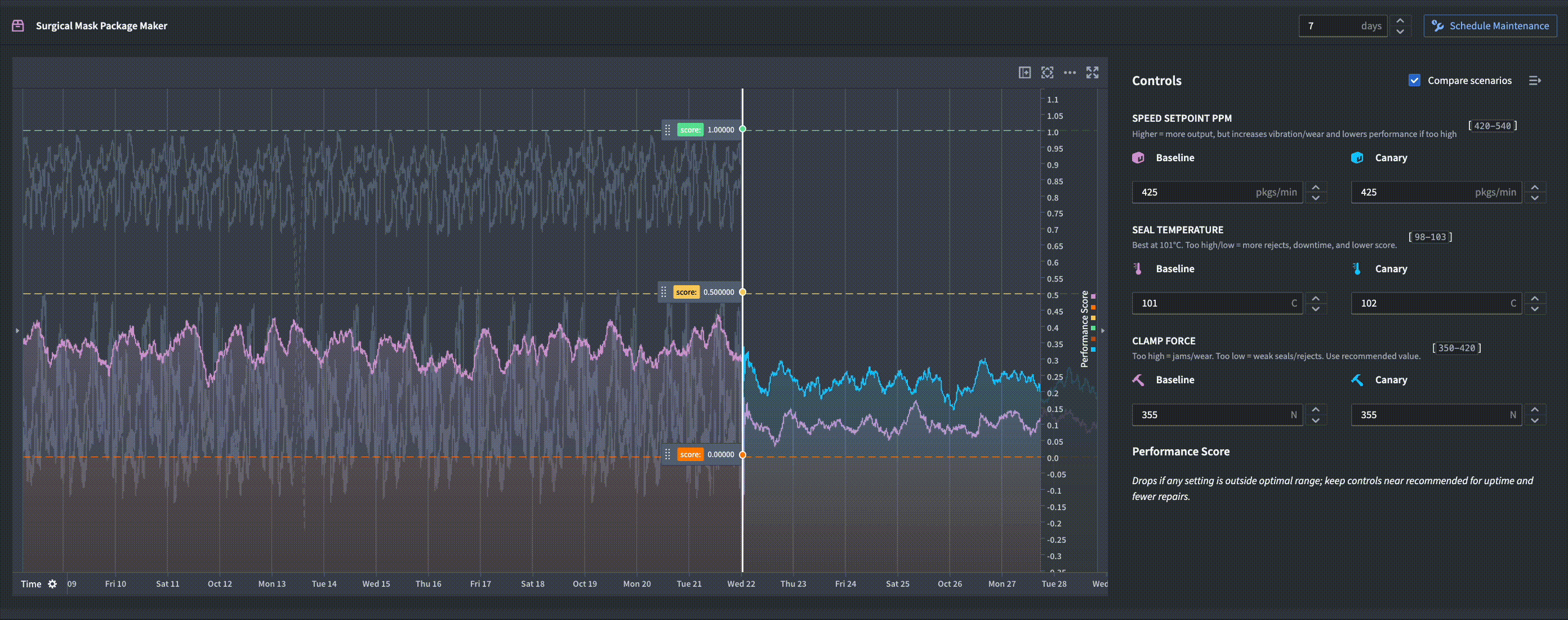
How it works
Function-backed time series require a Python Foundry function that returns a serialized numeric time series. When you query data, Quiver invokes your function with the specified parameters, dynamically generating the time series at query time. This output is then treated as a first-class time series within Foundry, allowing you to apply further operations and visualizations.
This integration makes it easy to incorporate custom models and on-the-fly analytics into your dashboards, enabling flexible and modular time series workflows.
Example use cases
- Forecasting and simulation: Generate forecasts using the libraries of your choice, such as Prophet or statsmodels, or use models built in Foundry to analyze future trends and perform scenario planning.
- Multivariate analysis: Combine outputs from several sensors or metrics to enable comprehensive time series analysis.
- Rapid model iteration: Quickly iterate on custom models without managing intermediate datasets or data pipelines.
Example: Use Prophet for forecasting
The example below demonstrates how to use Prophet ↗ with function-backed time series for forecasting.
Copied!1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24from functions.api import function from timeseries_sdk.types import TimeSeries from ontology_sdk.ontology.objects import Machine from prophet import Prophet @function def performance_prophet_forecast( machine: Machine, periods: int = 96, # number of future steps freq: str = "15min", # sampling frequency ) -> list[bytes]: """ Forecast a machine's performance_score using Prophet. """ df = machine.performance_score.to_pandas(all_time=True) if df.empty: return TimeSeries.serialize(df) df = df.rename(columns={"timestamp": "ds", "value": "y"}).sort_values("ds") model = Prophet().fit(df) future = model.make_future_dataframe(periods=periods, freq=freq, include_history=True) forecast = model.predict(future) out = forecast[["ds", "yhat"]].rename(columns={"ds": "timestamp", "yhat": "value"}) return TimeSeries.serialize(out)