Integrate geotemporal series with the Ontology
To establish a geotemporal series in the Ontology that drives analysis and visualization within Palantir applications, such as a Gaia map, you will use Pipeline Builder to:
- Create a geotemporal series sync using the geotemporal series output. The output will contain a geotemporal series reference property (GTSR) to capture movement over time.
- Create a geotemporal series object type using the object type pipeline output. The object type will contain the GTSR and static information about the tracked entity, such as a vessel's call sign or name.
- Map the geotemporal series reference property from your geotemporal series sync to your single geotemporal series object type.

If you plan to add data from the Ontology to a Foundry map and not Gaia, then you can use time series to view and analyze data associated with geospatial or geotemporal objects. Learn more about creating and managing a time series sync.
Contact Palantir Support with additional questions about which integration type you should use to index your geotemporal data into the Ontology based on your enrollment and specific use case.
Follow the instructions below to add a geotemporal series sync output as a reference to a geotemporal series object type.
Create a new pipeline in Pipeline Builder
- Navigate to Pipeline Builder and select the green New pipeline button.
- Name your pipeline and select a project where it will be saved.
- Choose Streaming pipeline before selecting Create pipeline.
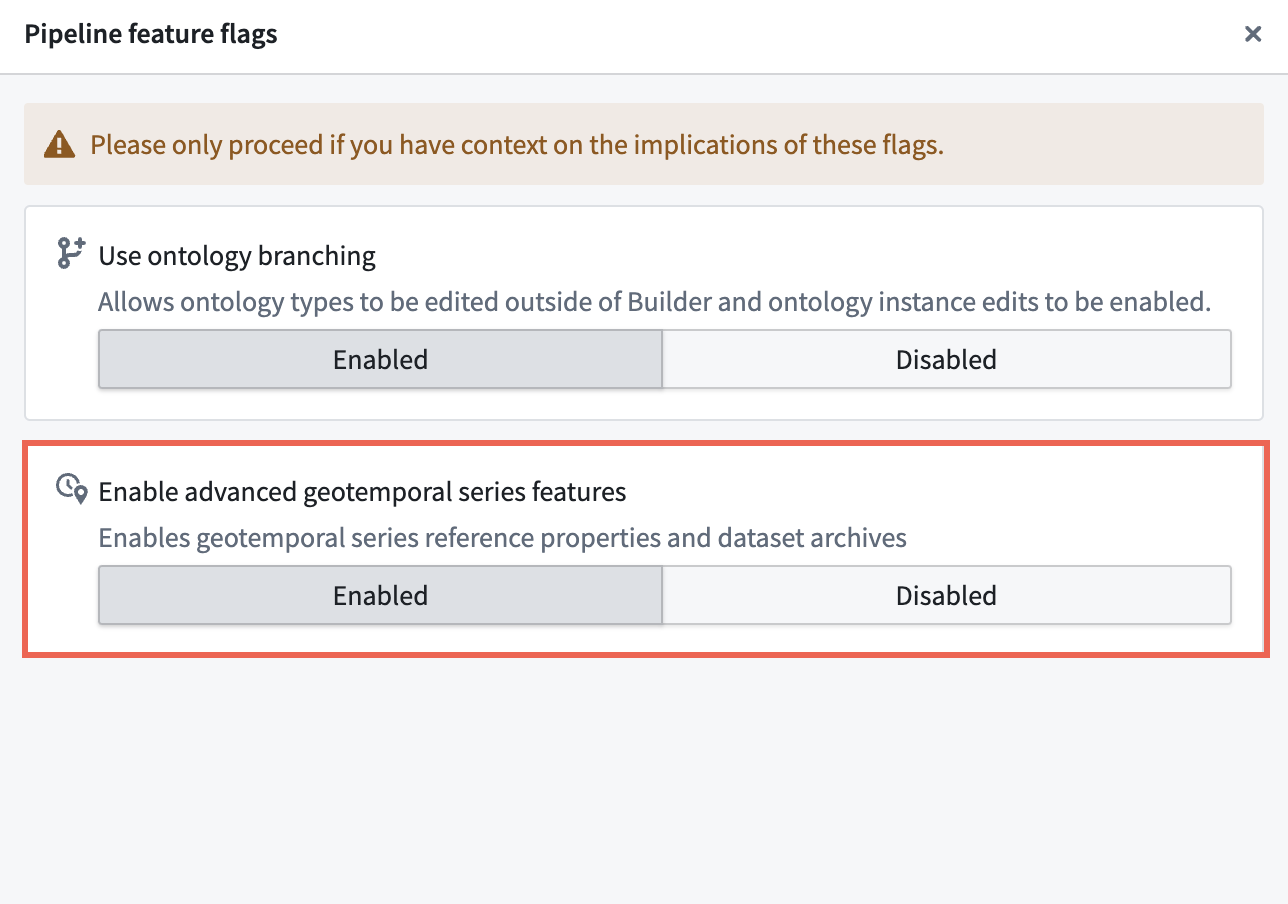
Enable advanced geotemporal series features
After creating a new, empty pipeline, toggle on Pipeline Builder's advanced geotemporal capabilities.
- Select Settings > Pipeline feature flags... from the top ribbon.
- Ensure that Enable advanced geotemporal series features is set to Enabled before you close out of the Pipeline feature flags window.
Import and transform your geotemporal datasets
Review the existing documentation on geotemporal data modeling before proceeding.
Identify the streaming and static datasets that will back your geotemporal series sync and object type and follow the instructions below to add them to your pipeline. While you can create both a geotemporal series object type and geotemporal series sync from one dataset, the steps below provide instructions using two: a live stream to back the geotemporal series sync and a static dataset to back the object type.
- Select Add Foundry data if you have already ingested your data into the platform.
- Search for your files in the Add data modal and select the + icon to add each dataset to your pipeline.
- Select Add data in the bottom right corner of the Add data modal.
![]()
Transform your streaming dataset
At a minimum, your streaming dataset should contain columns that capture a tracked entity's movement over time, such as its latitude and longitude at a given timestamp, as well as a string column that enables you to join the geotemporal series sync to the object type. Columns that contain data that changes over time are referred to as live fields, whereas those that remain consistent (such as an entity's name) are called static.
Your transform needs may vary depending on your streaming dataset's raw state upon ingest into Foundry. The example data outlined below contains the following columns that map to the sync's primary fields:
- Series_ID: A
stringcolumn used to join the geotemporal series sync to the static dataset-backed object type. Learn more about configuring a series ID. - Timestamp: A
timestampcolumn containing the time recorded for the entity's location. - Geopoint: A
geopointcolumn containing the entity's latitude and longitude pair.
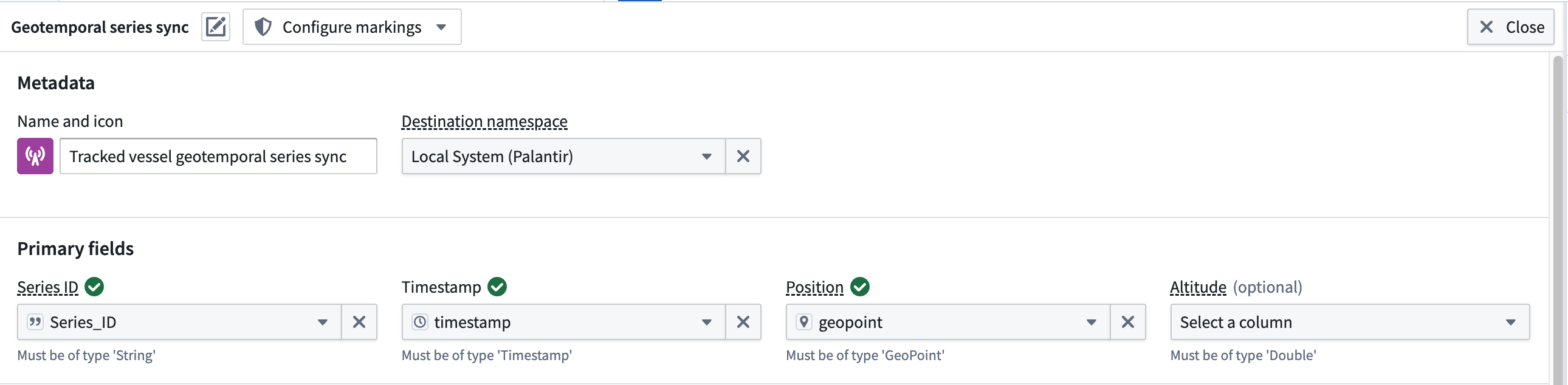
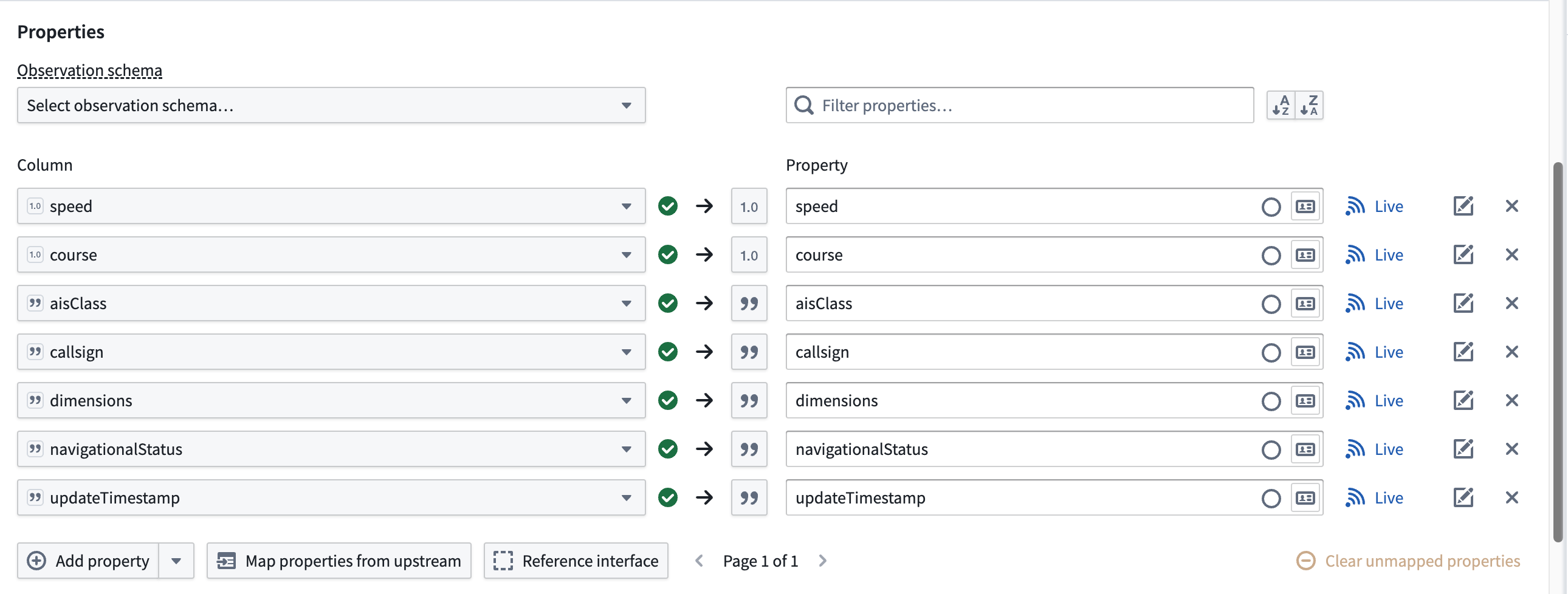
The dataset contains additional columns which will map to the geotemporal series sync's Properties but are not required for the sync to function in a Palantir map application.
If necessary, use Pipeline Builder's Cast and Create GeoPoint transforms to prepare your raw streaming dataset for output as a geotemporal series sync.
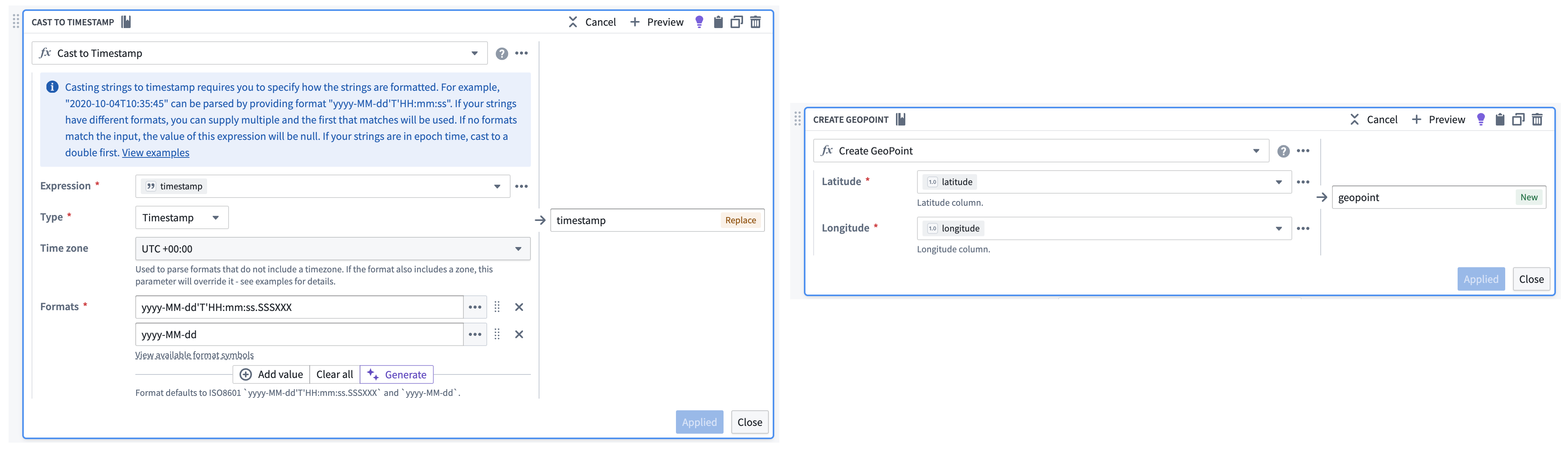
Follow the instructions below to create a geotemporal series sync output from your transformed streaming data:
- Select the streaming dataset or transform node to render the vertical menu bar, where you will choose the gold + icon to add a New geotemporal series sync output.
- Enter a name and optionally change the default icon for your sync in Name and icon.
- Select your Destination namespace to which Foundry will write the sync.
- Assign the relevant columns from your streaming dataset to the sync's Primary fields.
- Set your sync's Observation schema if one already exists. If one does not exist, then you can leave this field empty; Foundry will generate a new one from your sync's mapped properties. Learn more about observation schema.
- Optionally toggle the Live icon to the right of any additional Properties to mark one or multiple as static.

Foundry records a Live property value for every new observation, such as an entity's velocity at a given timestamp. If you mark a property as static, then Foundry records and applies the latest value of that property for all observations in the series.
- Optionally configure any Styles for your sync to control its downstream rendering.
- Optionally select Dataset archive in Advanced settings to retain all your sync's data in a long-term historical archive beyond the default live retention window of 14 days. You should select Dataset archive if you plan to visualize your objects on Foundry's Map application.
Contact Palantir Support with questions about expanding or contracting the default live retention window.
- Select Save to save your geotemporal series sync.
Transform your static dataset
At a minimum, your static dataset should contain the same unique identifier for the tracked entity as the streaming dataset, such as a name or call sign.
Next, you will transform your object type backing dataset to ensure it can be linked to your geotemporal series sync though a geotemporal series reference (GTSR).
- Select the static dateset in your pipeline and choose Transform to insert a new transform.
- Search for and select Apply expression.
- Select the input field labeled
Column, expression, or valueand choose your dataset's primary key column from Columns. In this example, the dataset'smmsicolumn contains a unique vessel identifier that can be used as the primary key. - Create a new column titled
Series_IDthat is a copy of the dataset's unique identifier, such asmmsi. You will use this new column to link your geotemporal series sync to the object type.

- Select Apply before saving the changes to your pipeline and previewing your data.

Create an object type output
After transforming your static dataset, follow the instructions below to create an object type output and implement the Tracked Entity interface.
- Select the transform node you just created to render the vertical menu bar, where you will choose the gold + icon to add a New object type output.

- Enter a name and optionally change the default icon for your sync in Name and icon.
- Select the ellipsis icon on the right side of a displayed property to set your primary key and title properties.

- Select the link icon next to your
Series_IDproperty to map the GTSR property to your object type by choosing Geotemporal series > From this pipeline.

If you do not see Geotemporal series as an option, verify that you have enabled Pipeline Builder's advanced geotemporal series features.
- Select Implement interface at the bottom of your screen and choose the
Tracked Entityinterface from the Palantir Core Ontology.

Contact Palantir Support to install the Tracked Entity interface on your enrollment if you are unable to access it in Ontology Manager.
- Choose Implement and go to mapping to navigate back to the object type creation window in Pipeline Builder before saving your changes.
Deploy your pipeline
After configuring your geotemporal series sync, creating an object type and interface, and establishing a link between the two via the GTSR, follow the instructions below to deploy your pipeline:
- Ensure all changes made to your pipeline are saved.
- Select Deploy to render the Deploy this pipeline panel.
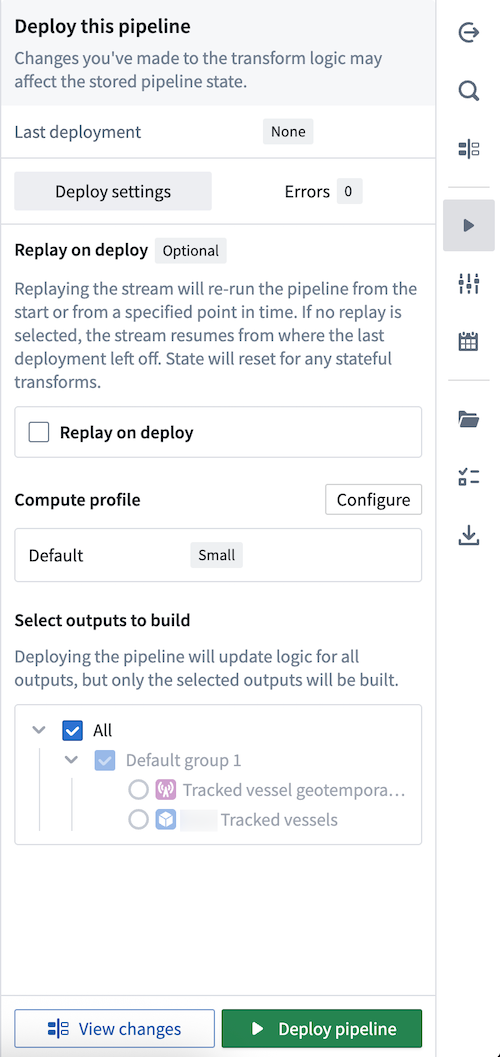
- Optionally Replay on deploy to re-run your pipeline from a specified point in time. Depending on your stream's size, replaying a pipeline may impact the pipeline's deployment speed. Learn more about additional options for streaming pipelines in Pipeline Builder.
- Select Deploy pipeline.
Once your pipeline deploys and your object type is created in your ontology, you can visualize its observations on a map.
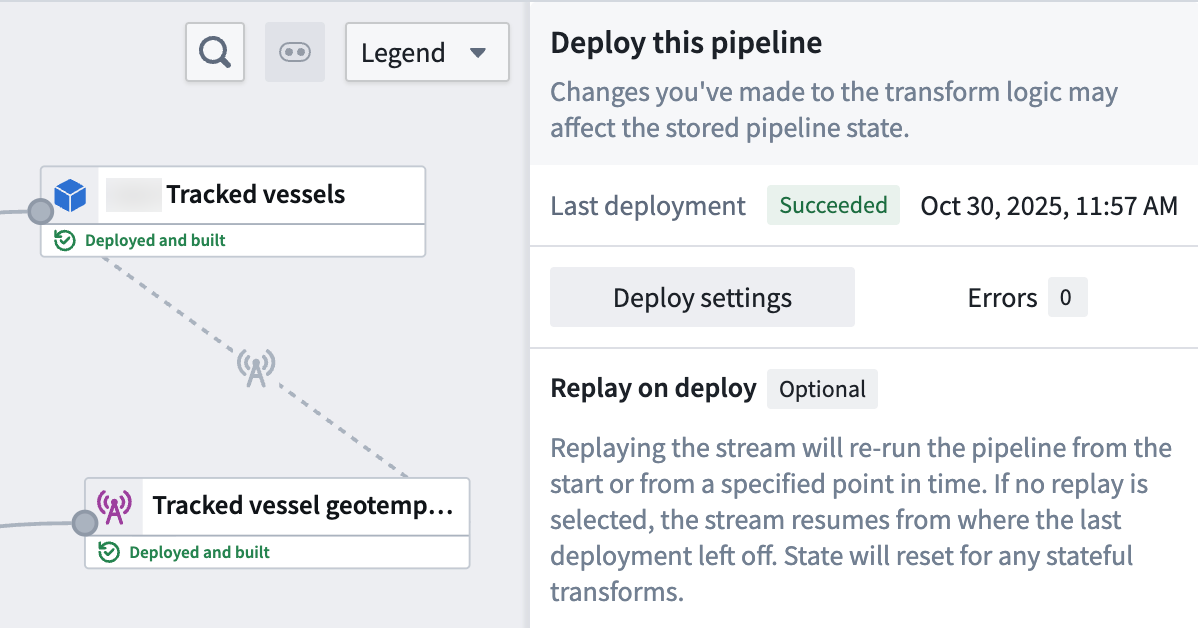
Visualize your geotemporal data
Gaia
Gaia is only accessible if your enrollment contains Gotham. Contact Palantir Support with questions about access to Gaia or its additional documentation available in platform.
To ensure Gotham can access object types in your Foundry ontology and render objects as part of a data layer on a Gaia map, you must follow the instructions to type map your object type in Ontology Manager.
To support Pipeline Builder's advanced geotemporal features, you must complete the type mapping process to discover your object type in Gotham even if your enrollment contains Map Rendering Service.
Once you ensure your object type is discoverable by Gotham, you can add it to your Gaia map.
In addition to adding data from your ontology, you can review the existing documentation to learn more about creating ontology data from Gaia.
Map
With your pipeline deployed, you can add your object type as a layer on a new or existing map in Foundry. Object data on a map will update in real-time when upstream changes are made, with those updates stored both within the object type and the sync's dataset archive.
The ability to view real-time geotemporal series object updates on a map may not be available on all enrollments. Contact Palantir Support to enable this feature if you are unable to view object updates from your geotemporal series object type after successful configuration and deployment in Pipeline Builder.
Learn more about visualizing data from your ontology in Foundry.